Overview
- Peptide CEPREVRRVQWPATQ(G), corresponding to amino acid residues 480-494 of rat Latrophilin-1 (Accession O88917). Extracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALR-021), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALR-021), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Latrophilin-1/LPHN1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-LR021).
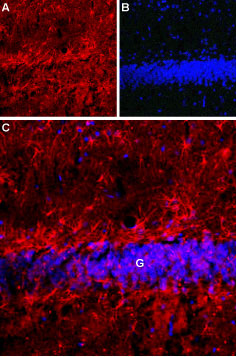 Expression of Latrophilin-1 receptor in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal dentate granule layer (G) using Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALR-021). A. Latrophilin-1 receptor staining (red) appears in astrocytes. B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain (blue). C. Merged image of A and B.
Expression of Latrophilin-1 receptor in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of rat hippocampal dentate granule layer (G) using Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALR-021). A. Latrophilin-1 receptor staining (red) appears in astrocytes. B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain (blue). C. Merged image of A and B.
 Expression of Latrophilin-1 receptor in SH-SY5Y cell lineCell surface detection of Latrophilin-1 receptor in intact living human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells with Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALR-021), (red), (1:50) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody. B. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue). C. Merged images of A and B.
Expression of Latrophilin-1 receptor in SH-SY5Y cell lineCell surface detection of Latrophilin-1 receptor in intact living human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells with Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALR-021), (red), (1:50) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody. B. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue). C. Merged images of A and B.
- Sugita, S. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 32715.
- Martinez, A.F. et al. (2011) Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B 156, 1.
- Matsushita, H. et al. (1999) FEBS Lett. 443, 348.
- Davletov, B.A. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271, 23239.
- Capogna, M. et al. (2003) J. Neurosci. 23, 4044.
- Lelyanova, V.G. et al. (2009) Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 147, 701.
- Silva, J.P. et al. (2011) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 12113.
- Levine, A. et al. (1994) Cell 77, 587.
- Tucker, R.P. and Chiquet-Ehrismann, R. (2006) Dev. Biol. 290, 237.
- Ichtchenko, K. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 5491.
Latrophilins (Latrophilin1-3) are members of the adhesion G-protein coupled receptor subfamily. Like all GPCRs, Latrophilins have seven transmembrane domains and are distinguished by a large extracellular N-terminal tail and a large intracellular C-terminal tail1. The N-terminus has several cell adhesion domains and undergoes proteolysis after synthesis, while the C-terminal has various consensus post-translational sites like phosphorylation and palmitoylation2. In addition, Latrophilins undergo alternative splicing3.
Latrophilin-1 was discovered by its ability to bind α-Latrotoxin (α-LTX), a toxin isolated from the black widow spider venom4. α-LTX induces exocytosis by creating a Ca2+ influx in the presynaptic membrane. α-LTX can also stimulate small vesicle exocytosis in a Ca2+ independent manner. Three receptors have been found to bind α-LTX. Of the three, Latrophilins are responsible for the Ca2+-independent effects of α-LTX2. The binding of α-LTX to Latrophilin-1 increases exocytosis of neurotransmitters5,6.
In an attempt to find the natural ligand of Latrophilin-1, Lasso, a splice variant of Teneneurin-2 was discovered to be an endogenous binding partner of the adhesion-GPCR7. Teneneurins are large glycoproteins with a single transmembrane domain8,9. Like Latrophilin-1, Teneneurins are mostly expressed in the brain where they modulate neurite outgrowth, axon guidance and synaptogenesis7.
Regarding the localization of Latrophilins, Latrophilin-1 is expressed predominantly in the brain, Latrophilin-2 is highly expressed in the liver and lung, while Latrophilin-3 is almost exclusively detected in the brain1,10.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Latrophilin-1 (LPHN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALR-021) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Latrophilin-1 from rat, human, and mouse samples.