Overview
- Peptide (C)KELSKTGDEKYIEE, corresponding to amino acid residues 587-600 of rat LETM1 (Accession Q5XIN6). Intracellular, mitochondrial matrix.
- Rat brain, mouse brain, human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (MOLT-4), and human colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29) (1:1500-1:7500).
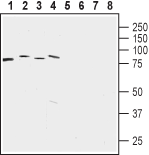 Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 5), mouse brain membrane (lanes 2 and 6), human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (MOLT-4) (lanes 3 and 7) and human colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29) cell lysates:1-4. Anti-LETM1 Antibody (#ANT-183), (1:1500).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 5), mouse brain membrane (lanes 2 and 6), human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (MOLT-4) (lanes 3 and 7) and human colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29) cell lysates:1-4. Anti-LETM1 Antibody (#ANT-183), (1:1500).
5-8. Anti-LETM1 Antibody, preincubated with LETM1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT183).
LETM1 (leucine zipper–EF hand-containing transmembrane region), a protein with a key role in mitochondrial volume homeostasis through regulation of K+/H+ exchange (KHE), is involved in respiratory chain biogenesis and in the pathogenesis of seizures in the Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS). LETM1 has been recently proposed to catalyze mitochondrial H+/Ca2+ exchange, which would imply a role in mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis as well.
LETM1 contains a hydrophobic N-terminal portion spanning the inner membrane and a large hydrophilic portion including the C-terminus located in the matrix. The primary amino acid sequence of the C-terminal part predicts at least two coiled-coil domains and two Ca2+-binding EF hand–like motifs. However, the EF hands differ from canonical EF hand motifs by several residues, and the α helices are not directly flanking the Ca2+-binding loop. The amino acid sequence of yeast LETM1 proteins lacks these putative Ca2+-binding EF hand motifs. The N-terminal region of the LETM1 protein superfamily displays a mitochondrial targeting sequence and a single transmembrane domain. The latter is highly conserved in all orthologues and is rich in proline residues.
In mitochondria, absence of LETM1, causes decompensation of electrophoretic K+, resulting in matrix swelling causing, in turn, increased mitophagy and/or cell death1.
