Overview
- Peptide (C)GRYDANLQ(S)ASPE, corresponding to amino acid residues 334-346 of mouse LRRTM1 (Accession Q8K377). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat and mouse brain lysates (1:400-1:800).
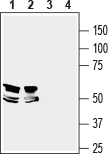 Western blot analysis of mouse brain (lanes 1 and 3) and rat hippocampus (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-LRRTM1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-141), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain (lanes 1 and 3) and rat hippocampus (lanes 2 and 4) lysates:1,2. Anti-LRRTM1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-141), (1:400).
3,4. Anti-LRRTM1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with LRRTM1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR141).
- Rat brain sections (1:200).
Leucine rich repeat transmembrane neuronal 1 (LRRTM1) is a synaptogenic, cell adhesion protein that contributes to the regulation of synapse density and synaptic transmission. The LRRTM family in mammals includes four postsynaptic proteins, which have been shown to interact with presynaptic neurexins and heparan sulphate proteoglycan glypican on the presynaptic side1.
In human and mouse genomes, LRRTM1 is encoded by a single exon and is predominantly expressed in the nervous system. LRRTM1 is a single-membrane-spanning transmembrane protein and its structure contains ten N-terminal LRR repeats, a single pass transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic C-terminal tail comprising a PDZ-binding motif1.
Mutations in human genes encoding the LRRTM proteins are implicated in cognitive disorders. In particular, LRRTM1 is associated to human handedness and schizophrenia1,2. Studies on Lrrtm1 knockout mice shows deficits in behavioral responses to stressful situations and novel objects, spatial memory and social discrimination deficits3. LRRTM1 mutant mice display impairment in visual behaviors, suggesting a functional role of LRRTM1 in retinothalamic convergence in vision4.
