Overview
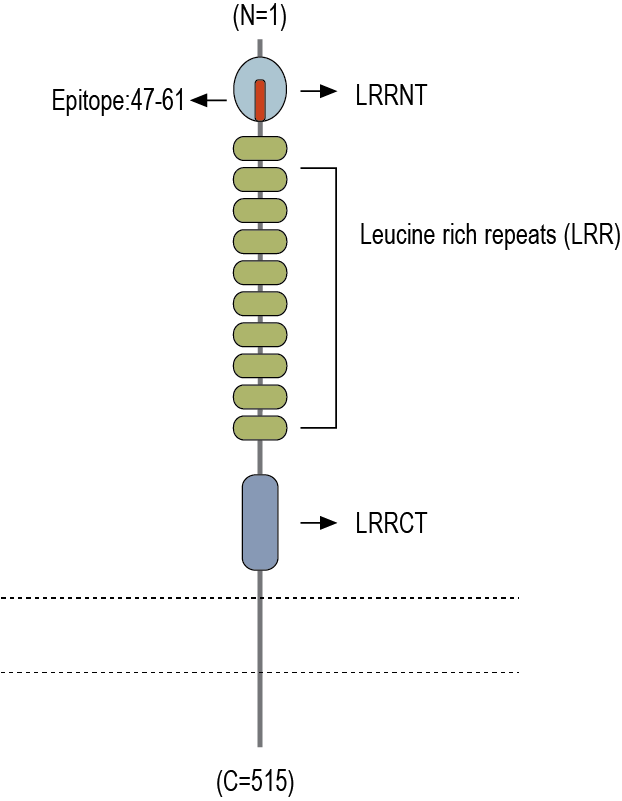
- Peptide CDSQGFHSVPNATDK, corresponding to amino acid residues 47 - 61 of mouse LRRTM2 (Accession Q8BGA3). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate:1. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:200).
2. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with LRRTM2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-NR142). Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:400).
2. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with LRRTM2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-NR142). Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysates:1. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysates:1. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:200).
2. Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with LRRTM2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-NR142).
 Expression of LRRTM2 in mouse parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:400), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. LRRTM2 immunoreactivity (green) appears in cortical neurons in layer 5 (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with LRRTM2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-NR142), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of LRRTM2 in mouse parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142), (1:400), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. LRRTM2 immunoreactivity (green) appears in cortical neurons in layer 5 (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with LRRTM2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-NR142), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Soler-Llavina, G. J. et al. (2013) Neuron., 79, 439.
- Yamagata, A. et al. (2018) Nat. Commun., 9, 3964.
- Bhouri, M. et al. (2018) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 115, 5382.
Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane neuronal proteins (LRRTMs) function as postsynaptic organizers that induce excitatory synapses. There are four related LRRTM genes in mammals, and all are enriched in brain and expressed from postnatal day one or earlier1.
LRRTM2 is the most synaptogenic isoform of the family, and its expression is strongly restricted to excitatory synapses in mature neurons. It consists of leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain in the N-terminal extracellular domain, followed by a single transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic region contains a PDZ domain binding motif2.
LRRTM2 can induce clustering of NMDA receptors, PSD-95 and SynGAP in postsynaptic membrane. PSD-95 function as a scaffold to cluster these postsynaptic proteins. It was found that LRRTM2 deletion in mice leading to dramatically impairs basal synaptic transmission and disrupts long-term potentiation, a prominent form of synaptic plasticity that is critical for learning and memory3. LRRTM2 responsible for the structural linkage mediating nanocolumn alignment of AMPARs, a protein critical for the strength of basal synaptic transmission3.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-LRRTM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-142) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize LRRTM2 from rat, mouse and human samples.
