Overview
- Peptide CAYNGDN(S)FKPMR, corresponding to amino acid residues 26-38 of mouse Lynx1 (Accession P0DP60). Extracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANC-021), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANC-021), (1:200).
3, 4. Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Lynx1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NC021). Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANC-021), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANC-021), (1:200).
3, 4. Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Lynx1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NC021).
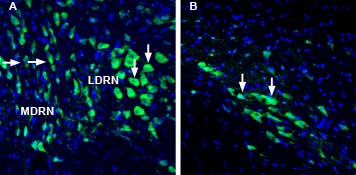 Expression of Lynx1 in rat dorsal raphe nucleus and substantia nigra pars compactaImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANC-021), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Lynx1 staining in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), (green) is detected in cells of the medial DRN (MDRN, horizontal arrows) and in cells of the lateral DRN (LDRN), (vertical arrows). B. Lynx1 immunoreactivity in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNC), (green) is observed in cells of the SNC (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of Lynx1 in rat dorsal raphe nucleus and substantia nigra pars compactaImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANC-021), (1:1000), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Lynx1 staining in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), (green) is detected in cells of the medial DRN (MDRN, horizontal arrows) and in cells of the lateral DRN (LDRN), (vertical arrows). B. Lynx1 immunoreactivity in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNC), (green) is observed in cells of the SNC (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Miwa, J.M. et al. (1999) Neuron 23, 105.
- Sadahiro, M. et al. (2016) J. Physiol. Paris 110, 29.
- Morishita, H. et al. (2010) Science 330, 1238.
- Vasilyeva, N.A. et al. (2017) Biochemistry (Mosc). 82, 1702.
Lynx1 is a member of the Ly-6/neurotoxin gene superfamily (Lynx family) of proteins that feature a three-looped toxin fold and a cysteine rich motif; structural characteristics that are shared with the snake venom toxin α-bungarotoxin1.
Lynx1 is expressed in large projection neurons in the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum. Initial analysis of the functional consequence of genetic ablation of Lynx1 in mice revealed that Lynx1 is an allosteric modulator of various nicotinic receptors that affects their kinetics, decreases their agonist affinities, and increases their desensitization to overall limit their activation. Lynx1 can serve as a protective measure against neurotoxicity through agonist-induced overstimulation2. In fact, deletion of Lynx1 eventually leads to neurodegeneration in aged mice3.
Collectively the findings regarding Lynx1 suggest a direct relationship between plasticity regulation and nicotinic signaling, and underline the significance of fine tuning of nicotinic tone to vastly control the development of brain functions.
Lynx1 activity was shown to be related to the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease as well as cholinergic activity in healthy and tumor cells of bronchial epithelium4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Lynx1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANC-021) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, indirect live cell flow cytometry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Lynx1 from rat, mouse, and human samples.

