Overview
- Peptide(C) RTLNPASKWSK, corresponding to amino acid residues 330-340 of rat M4 muscarinic receptor (Accession P08485). 3rd intracellular loop.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 2), mouse brain membrane (lane 3 and 5) and SH-SY5Y cell lysate (lanes 4 and 6):1,3,4. Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 2), mouse brain membrane (lane 3 and 5) and SH-SY5Y cell lysate (lanes 4 and 6):1,3,4. Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004), (1:200).
2,5,6. Anti-CHRM4 Antibody, preincubated with CHRM4 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-MR004).
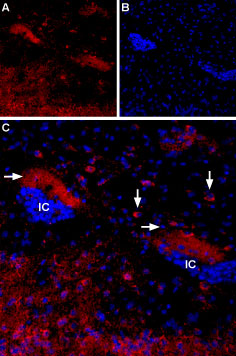 Expression of Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 in mouse islands of CallejaImmunohistochemical staining of mouse islands of Calleja (ventral striatum) using Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004). A. M4 mAChR staining (red) appears in soma of neuronal profiles (vertical arrows) and a diffuse halo (horizontal arrows) in the vicinity of the islands of Calleja (IC). B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain. C. Merged image of A and B.
Expression of Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 in mouse islands of CallejaImmunohistochemical staining of mouse islands of Calleja (ventral striatum) using Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004). A. M4 mAChR staining (red) appears in soma of neuronal profiles (vertical arrows) and a diffuse halo (horizontal arrows) in the vicinity of the islands of Calleja (IC). B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counterstain. C. Merged image of A and B.
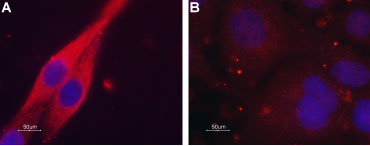 Expression of Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 in C6 transfected cellsImmunocytochemical staining of paraformaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized C6 cells. A. Transfected cells were stained using Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004), (1:100) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Non-transfected cells were stained using Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (1:100), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 in C6 transfected cellsImmunocytochemical staining of paraformaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized C6 cells. A. Transfected cells were stained using Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004), (1:100) followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Non-transfected cells were stained using Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (1:100), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
- Nathanson, N.M. (2008) Pharmacol. Ther. 119, 33.
- Migeon, J.C. and Nathanson N.M. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269, 9767.
- Ashkenazi, A. et al. (1987) Science 238, 672.
- Tietje, K.M. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 2828.
- Katz, A. et al. (1992) Nature 360, 686.
- Perez-Burgos, A. et al. (2010) Neuroscience 165, 293.
- Dorofeeva, N.A. et al. (2009) Neuroreport 20, 1386.
- Wickman, K. and Clapham, D.E. (1995) Physiol. Rev. 75, 865.
- Nesti, E. et al. (2004) Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 4073.
- Wessler, I. and Kirkpatrick, C.J. (2008) Br. J. Pharmacol. 154, 1558.
- Jongrye Jeon (2010) J Neurosci. 30(6): 2396–2405.
- Elizabeth Scarr (2012) CNS Neurosci Ther. 18(5): 369–379.
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter which activates two different groups of receptors: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) which belong to the superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels, and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR) which belong to the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. There are five separate gene products (M1-M5) that, assembled, make up this GPCR subfamily.
Generally, M1, M3 and M5 muscarinic receptors are known to activate phospholipase C (PLC) via Gq coupling, while M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors couple to Gi/o, and therefore inhibit adenylate cyclase1. This classification is however not clear cut. mAChR can activate adenylate cyclase by coupling to Gs2. In addition, M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors, when overexpressed, can also activate adenylate cyclase in some systems3-5.
Evidence suggests that muscarinic receptors can form homo- or heterodimers and that the dimer formed can subsequently affect the downstream signaling pathways1.
Muscarinic receptors have been shown to regulate voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, namely CaV2.16, as well acid sensing ion channels (ASIC)7. Generally speaking, the actions of muscarinic receptors on ion channels can be either via 2nd messengers or through their direct action on the channels once activated8.
Furthermore, muscarinic receptors can also promote endocytosis of ion channels (KV1.2 for example) by recruiting tyrosine kinases that phosphorylate the channel in order to terminate its activity9. Other diverse and important functions of muscarinic receptors include cell growth, survival and physiology1.
Expression of muscarinic receptors is found in neurons in the central nervous system as well as in the peripheral nervous system. These receptors are also expressed in cardiac and smooth muscle, lung, intestine, ovary and urothelium1,10. M4 muscarinic receptor is mostly expressed in the striatum where it colocalizes with D1 dopamine receptors11.
Malfunction of M4 muscarinic receptor is associated with a number of psychological and neurodegenerative diseases like Schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases12.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat M4 muscarinic receptor. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize M4 from rat, mouse, and human samples.

Multiplex staining of GluN1 and M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in mouse parietal cortexImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating mouse brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-CHRM4 Antibody (#AMR-004), (1:400) and Guinea pig Anti-NMDAR1 (GluN1) (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-001-GP), (1:1200). A. M4 muscarinic receptor staining (green). B. GluN1 staining (red) in same section. C. Merge of the two images reveals several cells expressing both M4 muscarinic receptor and GluN1 (arrows). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
