Overview
- Peptide (C)NSDSLTLEDQFIQHMD, corresponding to amino acid residues 102-117 of rat MC3R (Accession P32244). 1st extracellular loop.
- Mouse and rat brain lysate (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-MC3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AMR-023), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-MC3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AMR-023), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-MC3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with MC3 Receptor (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-MR023).
- Rat brain sections (frozen), (1:50).
- Human live intact promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell lines (1:40-1:80).
- The control antigen is not suitable for this application.
Melanocortin receptor 3 (MC3R) is one of five members of the melanocortin receptor family, which belongs to the 7-transmembrane domain, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily.
The ligands of these receptors, the melanocortins, are a group of structurally-related peptides comprising the α-, β-, and γ-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-, β-, γ-MSH) and the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), all of which are derived from post-translational processing of a common precursor peptide, proopiomelanocortin (POMC).1,2,3
One of the salient features of the melanocortin signaling system is the presence of two endogenous antagonists, proteins that bind specifically to the receptor and have an inhibitory effect. These antagonist proteins are termed agouti (or agouti signaling protein, ASP) and agouti-related protein (AGRP).1
All five melanocortin receptors bind their agonists (the melanocortins) and their endogenous antagonists (agouti and AGRP) with differing affinities. MC3R is the only one of the melanocortin receptors that shows no difference in binding specificity for any of the melanocortins, binding all of them with equal efficiency. AGRP is the high affinity endogenous antagonist of MC3R.1,2,3
The physiological function of MC3R is still poorly understood. The distribution of MC3R in hypothalamic nuclei of the central nervous system (CNS) suggests a role in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Indeed, studies with MC3R knockout (MC3R KO) mice showed that these mice have increased body fat due to increased feed efficiency.4 In humans, several polymorphisms of the MC3R gene are associated with high insulin levels and obesity in children.5 In addition, expression of MC3R in macrophages is thought to mediate the well known anti-inflammatory effects of α-MSH.6
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
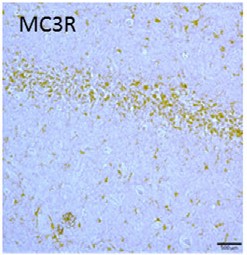
Expression of MC3R in rat hippocampus.Immunohistochemical staining of rat brain sections using Anti-MC3 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AMR-023). MC3R staining (brown) is detected in CA1 region.Adapted from Massey, A.T. et al. (2016) Front. Neurol. 7, 65. with permission of Frontiers.
