Overview
- Peptide (C)KPPIKRQDGELVGYR, corresponding to amino acid residues 402 - 416 of mouse MERTK (Accession Q60805). Extracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:400).
3, 4. Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with MERTK (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-TR033). Western blot analysis human HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse BV-2 microglia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:400).
Western blot analysis human HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse BV-2 microglia cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:400).
4-6. Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with MERTK (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-TR033).
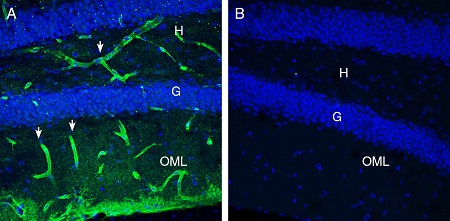 Expression of MERTK in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 (green). A. MERTK staining (green) in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus region is detected in blood vessel profiles (arrows) in the hilus (H) and outer molecular layer (OML). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with MERTK (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-TR033), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). G = Granule layer.
Expression of MERTK in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 (green). A. MERTK staining (green) in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus region is detected in blood vessel profiles (arrows) in the hilus (H) and outer molecular layer (OML). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with MERTK (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-TR033), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). G = Granule layer. Expression of MERTK in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:300), followed by goat anti rabbit conjugated with Alexa 488 (green). A. MERTK immunoreactivity appears in in blood vessel profiles (vertical arrows) in the molecular (M), purkinje (P) and granule (G) layers and in basket profiles (horizontal arrows) around Purkinje soma. B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with MERTK (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-TR033), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). G= Granule layer, P = Purkinje layer, M = Molecular layer.
Expression of MERTK in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:300), followed by goat anti rabbit conjugated with Alexa 488 (green). A. MERTK immunoreactivity appears in in blood vessel profiles (vertical arrows) in the molecular (M), purkinje (P) and granule (G) layers and in basket profiles (horizontal arrows) around Purkinje soma. B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with MERTK (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-TR033), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). G= Granule layer, P = Purkinje layer, M = Molecular layer. Multiplex staining of MERTK and Aquaporin 4 in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 and Guinea Pig Anti-Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) (300-314) Antibody (#AQP-014-GP), (1:300), followed by goat anti-guinea pig-AlexaFluor-594. A. MERTK immunoreactivity (greens) appears around blood vessels (arrows). B. Aquaporin 4 immunoreactivity (red) appears around blood vessels (arrows). C. Merge of the two images reveals several vessels that express both MERTK and AQP4 (arrows point at examples).
Multiplex staining of MERTK and Aquaporin 4 in rat parietal cortex.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 and Guinea Pig Anti-Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) (300-314) Antibody (#AQP-014-GP), (1:300), followed by goat anti-guinea pig-AlexaFluor-594. A. MERTK immunoreactivity (greens) appears around blood vessels (arrows). B. Aquaporin 4 immunoreactivity (red) appears around blood vessels (arrows). C. Merge of the two images reveals several vessels that express both MERTK and AQP4 (arrows point at examples).
- Graham, D.K. et al. (2014) Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 769.
- Kasikara, C. et al. (2017) Mol. Cancer Res. 15, 753.
- Huelse, J.M. et al. (2020) Pharmacol. Ther. 213, 107577.
- Cummings, C.T. et al. (2013) Clin. Cancer Res. 19, 5275.
Myeloid-epithelial-reproductive tyrosine kinase, MERTK, is a receptor tyrosine kinase of the TAM (Tyro3, Axl and MERTK) family, expressed in numerous cancers1.
The extracellular N-terminal domain contains two immunoglobulin-like and two fibronectin 3 domains, followed by a hydrophobic single pass transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic C-terminal tail containing a tyrosine kinase domain1,2.
Auto-phosphorylation induced by ligand binding influences a range of downstream signaling pathways and cellular functions2. The physiological roles of MERTK include regulation of tissue homeostasis and repair, innate immune control, and platelet aggregation. However, aberrant expression of this protein promotes neoplasia, cell cycle progression, proliferation and tumor growth, resistance to apoptosis, and promotion of tumor metastases.
MERTK is involved in the activation of several canonic oncogenic signaling pathways in various types of cancers including: leukemia, non-small cell lung cancer, glioblastoma, melanoma, prostate cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer and gastric cancer1,3,4.
Due to its pivotal role in cancer development and metastasis, multiple therapeutic approaches are currently in development to inhibit MERTK, including ligand "traps" and small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
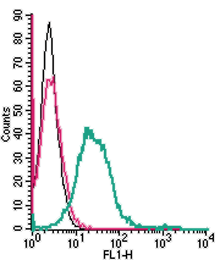
Anti-MERTK (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-033) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and live cell flow cytometry. It has been designed to recognize MERTK from human, rat, and mouse samples.