Overview
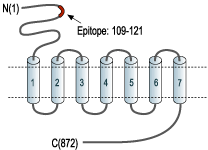
- Peptide SLSRGADGSRHIC, corresponding to amino acids 109-121 of rat mGluR2 (Accession P31421). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat cerebellum (lanes 1 and 3) and cortex (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat cerebellum (lanes 1 and 3) and cortex (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011), (1:400).
3,4. Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with mGluR2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GC011). Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011), (1:200).
2. Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with mGluR2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GC011).
 Expression of mGluR2 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed brain frozen sections using Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011). A. mGluR2 (green) is visualized in the corpus callosum (CC) and hippocampal stratum oriens (OR). B. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (red), a marker of astrocytes. C. Merge of the two images demonstrates expression of mGluR2 in astrocytes. DAPI is used as the nuclear counterstain (blue).
Expression of mGluR2 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed brain frozen sections using Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011). A. mGluR2 (green) is visualized in the corpus callosum (CC) and hippocampal stratum oriens (OR). B. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (red), a marker of astrocytes. C. Merge of the two images demonstrates expression of mGluR2 in astrocytes. DAPI is used as the nuclear counterstain (blue).
 Expression of mGluR2 in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of mGluR2 in live intact rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells with Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011), (1:100), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Live view of the cells. C. Merge of A and B.
Expression of mGluR2 in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of mGluR2 in live intact rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells with Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011), (1:100), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Live view of the cells. C. Merge of A and B.
- Flor, P.J. et al. (1995) Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 622.
- Conn, P.J. and Pin, J.P. (1997) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37, 205.
- Swanson, C.J. et al. (2005) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 4, 131.
L-Glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, operates through several receptors that are categorized as ionotropic (ligand-gated cation channels) or metabotropic (G-protein coupled receptors). The metabotropic glutamate receptor family includes eight members (mGluR1-8) that have been divided into three groups based on their sequence homology, pharmacology and signal transduction.
Group II of the metabotropic glutamate receptors includes the mGluR2 and mGluR3 receptors. The receptors present the typical G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) signature topology: seven transmembrane domains with a large extracellular N-terminus domain that contains the glutamate binding site, and an intracellular C-terminus.1,2 mGluR2 and mGluR3 are coupled to Gi/Go and hence inhibit cAMP formation following receptor activation.1,2
mGluR2 is widely distributed throughout the brain with high expression in several limbic areas including the cortex, hippocampus and amygdala. mGluR2 is localized primarily presynaptically, although postsynaptic localization has also been described.
In line with its presynaptic localization, mGluR2 is thought to function as an autoreceptor in a negative feedback mechanism that suppress further release of glutamate from the cell on which it is expressed.
The involvement of mGluR2 in neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission suggests that modulation of this receptor is a promising strategy for the treatment of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as anxiety, schizophrenia, and pain.3
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of rat mGluR2. The epitope is specific for mGluR2 and will not cross-react with the closely related mGluR3 channel. Anti-mGluR2 (extracellular) Antibody (#AGC-011) can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize mGluR2 from human, rat and mouse samples.
