Overview
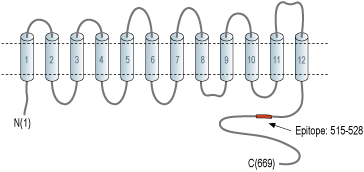
- Peptide (C)EHLGVPENERRTTK, corresponding to amino acid residues 515-528 of human NHE-6 (Accession Q92581). Intracellular, C-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and new born rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and new born rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody, preincubated with Na+/H+ Exchanger 6/NHE-6 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NX006). Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate:1. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate:1. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200).
2. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody, preincubated with Na+/H+ Exchanger 6/NHE-6 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NX006). Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200).
2. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody, preincubated with Na+/H+ Exchanger 6/NHE-6 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NX006).
 Expression of NHE-6 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. NHE-6 staining (green) in hippocampal dentate gyrus region, appears in neuronal soma outlines in the hilus (horizontal arrows) and the outer granule layer (vertical arrows). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of NHE-6 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections with Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006), (1:200), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. NHE-6 staining (green) in hippocampal dentate gyrus region, appears in neuronal soma outlines in the hilus (horizontal arrows) and the outer granule layer (vertical arrows). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
- Siyanov, V. and Baltz, J.M. (2013) Biol. Reprod. 88, 157.
- Ruffin, V.A. et al. (2014) Front. Physiol. 5, 43.
- Prasad, H. and Rao, R. (2015) J. Biol. Chem. 290, 5311.
Intracellular pH regulation in the brain is extremely important in both physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Changes in Intracellular pH often result in altered neuronal excitability. In mammalian cells, intracellular pH against acidosis is generally regulated by ion transporters located on the plasma membrane called sodium-hydrogen exchangers (Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE)1,2. In addition to their role in regulating pH, NHE transporters also function in a coupled mode to mediate recovery from decreased cell volume1.
Several studies have suggested that Na+/H+ exchange is the predominant pH-regulatory mode in isolated nerve terminals. In addition, Na+/H+ exchange plays a role in regulating synaptic transmission at glutamatergic, GABAergic, and dopaminergic synapses1.
The NHE family belongs to the Slc9 gene family of Na+ coupled transport proteins and comprises nine mammalian isoforms of Na+/H+ exchangers that are localized to the plasma membrane, NHE1-9 encoded by the SLC9A1-SLC9A9 genes, respectively. SLC9 family members have a short N terminus and an extensive C terminus that plays a regulatory role2.
NHE6 is localized to early and recycling endosomes, where it exchanges luminal H+ for Na+ or K+. Its expression is highest in the spinal cord and brain and is particularly enriched in the hippocampus, cortex, and Purkinje cell layer of the cerebellum3. Mutations in NHE6 encoding gene have been linked to autism, Christianson syndrome, and Angelman-like syndrome.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 6 (NHE-6) Antibody (#ANX-006) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize NHE-6 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
