Overview
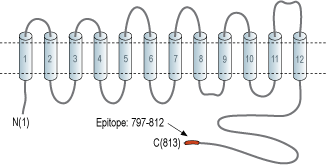
- Peptide (C)RASEPGNRKGRLGNEK, corresponding to amino acid residues 797-812 of rat NHE-2 (Accession P48763). Intracellular, C-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat kidney membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse kidney lysates (lanes 2 and 5) and rat stomach lysates (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 2 (NHE-2) Antibody (#ANX-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat kidney membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse kidney lysates (lanes 2 and 5) and rat stomach lysates (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 2 (NHE-2) Antibody (#ANX-002), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 2 (NHE-2) Antibody, preincubated with Na+/H+ Exchanger 2/NHE-2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NX002). Western blot analysis of human Colo-205 colorectal carcinoma cell lysates:1. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 2 (NHE-2) Antibody (#ANX-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Colo-205 colorectal carcinoma cell lysates:1. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 2 (NHE-2) Antibody (#ANX-002), (1:200).
2. Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 2 (NHE-2) Antibody, preincubated with Na+/H+ Exchanger 2/NHE-2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NX002).
- Counillon, L. and Pouyssegur, J. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 1.
- Kemp, G. et al. (2008) Channels 2, 329.
- Counillon, L. et al. (1994) Biochemistry 33, 10463.
- Tse, C. et al. (1994) Biochemistry 33, 12954.
- Paris, S. and Poouyssegur, J. (1983) J. Biol. Chem. 258, 3503.
- Aronson, P.S. et al. (1983) J. Biol. Chem. 258, 6767.
- Yu, F.H. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268, 25536.
- Aronson, P.S. et al. (1982) Nature 299, 161.
- Bookstein, C. et al. (1997) Am. J. Physiol. 273, 1496.
- Chambrey, R. et al. (1998) Am. J. Physiol. 275, 379.
- Schultheis, P.J. et al. (1998) Nat. Genet. 19, 282.
- Malakooti, J. et al. (1999) Am. J. Physiol. 277, 383.
In order to function in optimal conditions, cells must maintain a close to neutral intracellular pH. They have adopted various mechanisms in order to do so, one of which is via Na+/H+ exchangers (NHEs). Genes belonging to this group are expressed along a very broad range of organisms and are essential for protecting cells against intracellular acidification1.
To date, nine genes have been identified in mammals; NHE1-9. These membrane proteins have 10-12 transmembrane domains depending on whether a splice variant is expressed and an intracellular N-terminal. The C-terminal domain can be either intracellular or extracellular, also depending whether a splice variant of the protein is involved. The C-terminal part of the protein also undergoes posttranslational modification such as phosphorylation2. Both NHE-1 and NHE-2 have an extracellular loop which is glycosylated1,3,4.
Under physiological conditions, the Na+/H+ exchanger mediates the exchange of one extracellular Na+ ion for one intracellular proton, thereby keeping the overall charge neutral1. The extracellular binding site of Na+ is not selective as it can also bind Li+ and H+ 1,5,6. K+ ions inhibit NHE-1 but have no effect on NHE-27. The activation of NHE-1 and NHE-2 is sensitive to intracellular acidic pH. Under physiological conditions, both exchangers are not active and upon a drop of intracellular pH, they are rapidly activated1,5,8.
NHE-2 is detected in the intestine, kidney and parietal cells2,9-11. It is also detected in skeletal muscle and testis2,12.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Na+/H+ Exchanger 2 (NHE-2) Antibody (#ANX-002) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize NHE-2 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Human Barrett's esophageal cell lysate (1:200).
Laczko, D. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 311, G16.

