Overview
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
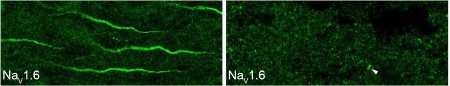
Knockout Validation of Anti-NaV1.6 (SCN8A) Antibody in mouse brain.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Anti-NaV1.6 (SCN8A) Antibody (#ASC-009). NaV1.6 staining (green) in neocortex is strongly observed in axonal initial segments. Note that NaV1.6 staining is abolished in brain sections from NaV1.6-/- mice (right panel).Adapted from Tian, C. et al. (2014) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 8, 297. with permission of Frontiers.
Specifications
- Peptide CIANHTGVDIHRNGDFQKNG, corresponding to amino acid residues 1042-1061 of rat NaV1.6 (Accession O88420). Intracellular loop between domains II and III.
Applications
- Rat brain lysates (1:200-1:1000).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane:1. Anti-NaV1.6 (SCN8A) Antibody (#ASC-009), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane:1. Anti-NaV1.6 (SCN8A) Antibody (#ASC-009), (1:200).
2. Anti-NaV1.6 (SCN8A) Antibody, preincubated with Nav1.6/SCN8A Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SC009).
- Mouse hippocampus.
Human cervical tissue (1:25) (Hernandez-Plata, E. et al. (2012) Int. J. Cancer 130, 2013.).
- Rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) primary culture (1:100).
Human cervical cancer cell line (1:25) (Hernandez-Plata, E. et al. (2012) Int. J. Cancer 130, 2013.).
Scientific Background
Voltage-gated sodium channels (NaV) are essential for the generation of action potentials and for cell excitability.1 NaV channels are activated in response to depolarization and selectively allow flow of Na+ ions. To date, nine NaV α subunits have been cloned and named NaV1.1-NaV1.9.4-5 The NaV channels are classified into two groups according to their sensitivity to tetrodotoxin (TTX): TTX-sensitive (NaV1.1, NaV1.2, NaV1.3, NaV1.4, NaV1.6 and NaV1.7) and TTX-resistant (NaV1.5, NaV1.8 and NaV1.9).2-3
Mammalian sodium channels are heterotrimers composed of a central, pore-forming α subunit and two auxiliary β subunits. Expression of the α subunit isoform is developmentally regulated and tissue specific. Sodium channels in the adult central nervous system and heart contain β1 through β4 subunits, whereas sodium channels in adult skeletal muscle have only the β1 subunit.6,7
NaV1.6 is highly expressed in the adult brain and localized at high density in Nodes of Ranvier and axon initial segments and at lower density in dendrites and cell bodies of some neurons. NaV1.6 channels are also expressed at high levels in cerebellar Purkinje neurons.8-11
