Overview
- Peptide (C)KIQKKPGKSELRINK, corresponding to amino acid residues 87-101 of human Neuregulin-1 (Accession Q02297). Extracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat and mouse heart lysates, mouse brain lysate, human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate, human U87-MG glioblastoma cell lysate, and human MDA-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate (1:200-1:1000).
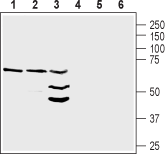 Western blot analysis of rat heart lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse heart membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-NRG1 (Neuregulin-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-111), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat heart lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse heart membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-NRG1 (Neuregulin-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-111), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-NRG1 (Neuregulin-1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with NRG1/Neuregulin-1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR111). Western blot analysis of human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 1 and 4), human U87-MG glioblastoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human MDA-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-NRG1 (Neuregulin-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-111), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 1 and 4), human U87-MG glioblastoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human MDA-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-NRG1 (Neuregulin-1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-111), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-NRG1 (Neuregulin-1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with NRG1/Neuregulin-1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR111).
- Rat brain sections (1:1000).
ErbB receptors are a family of tyrosine kinase receptors encoded by the erbB gene. These receptors commence signaling pathways such as the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and inositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways and have an important role in the control of cell growth and survival1. Neuregulins are a family of EGF-like factors that are produced from alternative RNA splicing of the same gene. Through their interaction with ErbB receptors, Neuregulins regulate normal developmental processes, plasticity, and oncogenesis2.
Neuregulin-1 is one of the four known proteins of the Neuregulin family and can be found in many organs including the heart, breast, peripheral and central nervous system. Neuregulin-1 is encoded by a gene located on chromosome 8p13 which produces more than 15 different isoforms of the same protein. All isoforms contain a core EGF domain encoded by exon E130 but other elements of the protein vary. Most NRG1 isoforms are synthesized as transmembrane proproteins which undergo proteolytic cleavage processes3.
Due to its important function in the central and peripheral nervous system as well as in other organs NRG1 has been implicated in a variety of pathologies. The NRG1 gene is suspected as a schizophrenia susceptibility gene. Mice with a mutated NRG1 exhibit elevated activity in open field and abnormal sensorimotor gating which correspond with schizophrenic like behavior in humans. These affects are reversed using anti-psychotic drugs4. In addition, Activation of NRG1 was found to improve cardiac survival and function in a rat and canine model of dilated and ischemic hearts5.
