Overview
- Peptide (C)KPRHQKDAKHPQMIK, corresponding to amino acid residues 546-560 of rat Neurexin 1α (Accession Q63372). Extracellular, N-terminus.

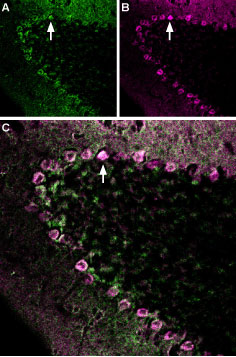 Multiplex staining of Neurexin 1α and GABA(A) ε Receptor in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum frozen section using Anti-Neurexin 1α (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ANR-031-AG) and Anti-GABA(A) ε Receptor (GABRE) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-633 Antibody (#AGA-015-FR). A. Nrxn1α staining (green). B. GABA(A) ε receptor staining (purple). C. Merge of the two images suggests extensive co-localization in Purkinje cells (arrow).
Multiplex staining of Neurexin 1α and GABA(A) ε Receptor in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum frozen section using Anti-Neurexin 1α (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ANR-031-AG) and Anti-GABA(A) ε Receptor (GABRE) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-633 Antibody (#AGA-015-FR). A. Nrxn1α staining (green). B. GABA(A) ε receptor staining (purple). C. Merge of the two images suggests extensive co-localization in Purkinje cells (arrow).
- Ichtchenko, K. et al. (1995) Cell 81, 435.
- Mosedale, M. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 6350.
- Ullrich, B. et al. (1995) Neuron 14, 497.
- Zhang, C. et al. (2010) Neuron 66, 403.
- Laarakker, M.C. et al. (2010) PLoS One 7, e31503.
Neurexins (NRXNs) are a family of transmembrane, synaptic adhesion molecules. NRXNS were identified as receptors for α-latrotoxin, a presynaptic toxin that triggers massive neurotransmitter release1. Neurexins are largely presynaptic proteins that form a trans-synaptic cell-adhesion complex with postsynaptic neuroligins2. They are encoded by three genes (NRXN1, NRXN2 and NRXN3), each using an upstream promoter to produce the longer α-isoform (α-NRXNs) and a downstream promoter to generate a shorter β-isoform (β- NRXNs).
The α- and β-isoforms of each neurexin are single-pass transmembrane proteins maintaining identical transmembrane and intracellular domains but having distinct extracellular domains. NRXNs in neurons localize to the presynaptic membrane and bind trans-synaptically to postsynaptic adhesion molecules and receptors3. Neurexins are expressed in all neurons, and are subject to extensive alternative splicing, generating >1,000 splice variants, some of which exhibit highly regulated developmental and spatial expression patterns4.
The extracellular domain of neurexin 1α (NRXN1α) is composed of three neurexin repeats (I, II, and III), which each contains the modules LNS-EGF-LNS. NRXN1α binds endogenous ligands including neuroligins, LRRTM family members, neurexophilin, α-dystroglycan, and GABA(A) receptors.
NRXN1α gene mutations have been identified in neuropsychiatric diseases including Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorder5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Neurexin 1α (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-031) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize Nrxn1α from rat, mouse and human samples.
Anti-Neurexin 1α (extracellular)-ATTO-488 Antibody (#ANR-031-AG) is directly labeled with an ATTO-488 fluorescent dye. ATTO dyes are characterized by strong absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield, and high photo-stability. The ATTO-488 label is analogous to the well known dye fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and can be used with filters typically used to detect FITC. Anti-Neurexin 1α (extracellular)-ATTO-488 Antibody has been tested in immunohistochemistry applications and is especially suited for experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.
