Overview
- Peptide CMIEWPEHPNRTYEK, corresponding to amino acid residues 180-194 of rat NK1 receptor (Accession P14600). 2nd extracellular loop.
 Expression of NK1 receptor in rat colonImmunohistochemical staining of rat colon paraffin-embedded section using Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (1:100). A. NK1 receptor labeling (green) appears in the tubular glands of the mucosa layer. B. Nuclear staining using DAPI. C. Merge of panels A. and B.
Expression of NK1 receptor in rat colonImmunohistochemical staining of rat colon paraffin-embedded section using Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (1:100). A. NK1 receptor labeling (green) appears in the tubular glands of the mucosa layer. B. Nuclear staining using DAPI. C. Merge of panels A. and B. Multiplex staining of VGLUT2 and Neurokinin 1 Receptor in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) sections using Anti-VGLUT2-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AGC-036-AR), (1:60) and Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (1:60). A. VGLUT2 staining (red). B. NK1 receptor staining (green). C. Merge of the two images demonstrates co-localization in some neuronal bodies (arrows point at examples). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of VGLUT2 and Neurokinin 1 Receptor in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) sections using Anti-VGLUT2-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AGC-036-AR), (1:60) and Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (1:60). A. VGLUT2 staining (red). B. NK1 receptor staining (green). C. Merge of the two images demonstrates co-localization in some neuronal bodies (arrows point at examples). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Multiplex staining of NK1 Receptor and mGluR5 in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of rat dorsal root ganglion using Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (green), (1:60) and Anti-mGluR5 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AGC-007-AR), (red), (1:60). A. NK1 receptor staining. B. mGluR5 staining appears in both cells (horizontal arrow) and fibers (vertical arrow). C. Merge of A and B demonstrates the co-localization of NK1 and mGluR5 receptors. Nuclei staining using DAPI as the counterstain (blue).
Multiplex staining of NK1 Receptor and mGluR5 in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of rat dorsal root ganglion using Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (green), (1:60) and Anti-mGluR5 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AGC-007-AR), (red), (1:60). A. NK1 receptor staining. B. mGluR5 staining appears in both cells (horizontal arrow) and fibers (vertical arrow). C. Merge of A and B demonstrates the co-localization of NK1 and mGluR5 receptors. Nuclei staining using DAPI as the counterstain (blue).
- Pennefather, J.N. et al. (2004) Life Sci. 74, 1445.
- Hershey, A.D. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 4366.
- Gerard, N.P. et al. (1993) Regul. Pept. 43, 21.
- Caberlotto, L. et al. (2003) Eur. J. Neurosci. 17, 1736.
- Munoz, M. et al. (2011) Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 15, 889.
- Ebner, K. et al. (2009) Curr. Pharm. Des. 15, 1647.
- May, A. and Goadsby, P.J. (2001) Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 10, 673.
- Palecek, J. et al. (2003) Neuroscience 116, 565.
Substance P (SP), Neurokinin A (NKA) and Neurokinin B (NKB) are all peptides belonging to the Tachykinin protein family. These three peptides, which demonstrate quite a heterogeneity in their distribution, exert their effect via three receptors: Neurokinin 1-3 receptors, members of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily. However, Neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor preferentially binds Substance P, Neurokinin 2 (NK2) receptor to NKA, and Neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor to NKB1.
Neurokinin receptors are distinguished by their seven transmembrane domains, an extracellular N-terminus and a cytosolic C-terminal. An unusual property of these receptors is the presence of introns as part of their structural organization1-3. Tachykinin receptors undergo alternative splicing. For example, NK1 receptor is detected with different C-terminal lengths. The longer receptor isoform is found in the brain whereas the truncated form is mostly detected in the periphery1,4.
Due to the broad expression profile of tachykinin peptides, their respective receptors are also expressed in a similar fashion. NK1 receptor is widely expressed in neurons, endothelial cells, muscle and immune system cells. NK2 receptor is broadly expressed in the periphery and its expression in the brain is quite restricted. NK3 receptor on the other hand is largely expressed in the central nervous system and is also detected in the uterus, skeletal muscle, lung and liver1.
Neurokinin receptors have been found in many pathophysiological indications and have therefore become targets for the development of pharmacological compounds. Such indications include cancer, psychological disorders, migraine and various inflammations, just to name a few5-8.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular) Antibody (#ATR-001) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, indirect live cell flow cytometry, and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize NK1 receptor from rat, mouse, and human samples.
Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG) is directly labeled with an ATTO-488 fluorescent dye. ATTO dyes are characterized by strong absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield, and high photo-stability. The ATTO-488 label is analogous to the well known dye fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and can be used with filters typically used to detect FITC. Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody is especially suited for experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.
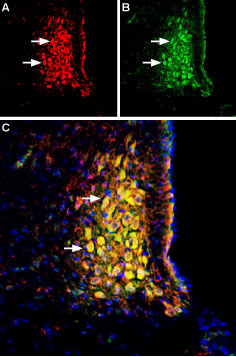 Multiplex staining of Noradrenaline Transporter (NET) and Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) in rat brain stem.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections using Anti-Noradrenaline Transporter (NET) (extracellular) Antibody (#AMT-002), (1:400) and Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (1:80). A. NET staining (red) in section of rat locus coeruleus. B. NK1 receptor staining (green) in same section. C. Merge of the two images reveals several cells expressing both NET and NK1 receptor (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of Noradrenaline Transporter (NET) and Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) in rat brain stem.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections using Anti-Noradrenaline Transporter (NET) (extracellular) Antibody (#AMT-002), (1:400) and Anti-Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ATR-001-AG), (1:80). A. NET staining (red) in section of rat locus coeruleus. B. NK1 receptor staining (green) in same section. C. Merge of the two images reveals several cells expressing both NET and NK1 receptor (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Applications
Citations
- Flow cytometry of mouse purified T-cells. Tested in NK1R-/- mice.
Morelli A.E. et al. (2020) Cell Rep. 30, 3448.
- Mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) (1:100).
Morelli A.E. et al. (2020) Cell Rep. 30, 3448.
- Mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) (1:100).
Morelli A.E. et al. (2020) Cell Rep. 30, 3448.
- Mouse purified T-cells. Tested in NK1R-/- mice.
Morelli A.E. et al. (2020) Cell Rep. 30, 3448.

