Overview
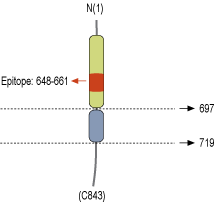
- Peptide (C)KVPSTDITLRPTRK, corresponding to amino acid residues 648-661 of rat NLGN1 (Accession Q62765). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035), (1:800).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain lysates:1,2. Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035), (1:800).
3,4. Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody preincubated with Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR035).
 Expression of NLGN1 in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of adult rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) using Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035) followed by anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody. A. NLGN1 labeling (red) appears in the cell bodies of the DRG neurons. B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counter stain (blue). C. Merged image of A and B.
Expression of NLGN1 in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of adult rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) using Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035) followed by anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody. A. NLGN1 labeling (red) appears in the cell bodies of the DRG neurons. B. Nuclear staining using DAPI as the counter stain (blue). C. Merged image of A and B. Expression of NLGN1 in rat hippocampus and cortexImmunohistochemical staining of free floating frozen section of rat hippocampal CA1 region (A, B) and rat parietal cortex (C, D) using Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035), (1:300). A. NLGN1 staining (green) appears in several neuronal profiles in the pyramidal layer (arrows). C. NLGN1 staining (green) is detected in several neuronal profiles including pyramidal cells and their apical dendrite (arrows). B, D. Nuclei are stained using DAPI as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of NLGN1 in rat hippocampus and cortexImmunohistochemical staining of free floating frozen section of rat hippocampal CA1 region (A, B) and rat parietal cortex (C, D) using Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035), (1:300). A. NLGN1 staining (green) appears in several neuronal profiles in the pyramidal layer (arrows). C. NLGN1 staining (green) is detected in several neuronal profiles including pyramidal cells and their apical dendrite (arrows). B, D. Nuclei are stained using DAPI as the counterstain (blue).
 Expression of NLGN1 in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of NLGN1 in intact living rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035), (1:100) followed by anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Merge of staining with live view of the cells.
Expression of NLGN1 in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of NLGN1 in intact living rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035), (1:100) followed by anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (red). B. Merge of staining with live view of the cells.
- Scheiffele, P. et al. (2000) Cell 101, 657.
- Sudhof, T.C. et al. (2008) Nature 455, 903.
- Bottos, A. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 20782.
- Fabrichny, I.P. et al. (2007) Neuron 56, 979.
- Arac, D. et al. (2007) Neuron 56, 992.
The NLGN1 gene encodes a member of a family of neuronal cell surface proteins. Neuroligins act as ligands for β-neurexins, cell adhesion proteins located presynaptically. Neuroligin and β-neurexin "shake hands," resulting in the connection between the two neurons and the production of a synapse. Neuroligin 1 may be involved in the formation and remodeling of central nervous system synapses1.
Proteins of this family may also mediate signaling by recruiting and stabilizing key synaptic components. This is done by interacting with other postsynaptic proteins to localize neurotransmitter receptors and channels in the postsynaptic density as the cell matures1.
Mutations in the neuroligin genes are implicated in autism and other cognitive disorders2.
Neuroligins have been found to play a role in angiogenesis, specifically in human pheripheral tissues3.
Neuroligins bind with the help of Ca2+ to the α-neurexin LNS (laminin, neurexin and sex hormone-binding globulin-like folding units) domains and to the β-neurexin LNS domain which then establishes a heterophilic trans-synaptic recognition code4. This binding results in a heterotetramer made up of a neuroligin-1 dimer and two neurexin-1 β monomers5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of rat Neuroligin 1. Anti-Neuroligin 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-035) can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize NLGN1 from rat, mouse and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Rat brain lysate (1:5000).
Ohta, K.I. et al. (2020) Behav. Brain. Res. 379, 112306.
