Overview
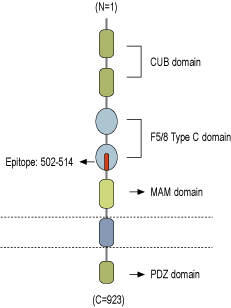
- Peptide (C)GGKHRENKVFMRK, corresponding to amino acid residues 502-514 of human neuropilin-1 (Accession O14786). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Cell surface detection of Neuropilin-1 by direct flow cytometry in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of Neuropilin-1 by direct flow cytometry in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ANR-063-F), (2.5µg). Cell surface detection of Neuropilin-1 by direct flow cytometry in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of Neuropilin-1 by direct flow cytometry in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti- Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ANR-063-F), (2.5µg).
Neuropilins (NRPs) are co-receptors for class 3 semaphorins, polypeptides with key roles in axonal guidance, and for members of the VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) family of angiogenic cytokines.
Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein and comprises a large extracellular region containing multiple domains, a single transmembrane domain and a small cytoplasmic domain, also with a number of protein interacting domains.
Class 3 semaphorins bind NRP1 (and NRP2) with different, and partially overlapping, specificities and affinities. Plexin A1 and Plexin A2 are the major signaling receptors for class 3 semaphorins, and complex with NRPs and semaphorins to form a holoreceptor essential for mediating effects of semaphorins on growth-cone collapse and axonal guidance in neurogenesis. The major VEGF-A signaling receptor, VEGF receptor 2, forms complexes with NRP1 and is important for optimal VEGFR2 signaling and function in endothelial cells.
Targeted disruption of the NRP1 gene has demonstrated an essential dual role of these molecules in neurogenesis and cardiovascular development. NRP1-null mice die with a spectrum of cardiovascular and neuronal defects1.
