Overview
- Peptide (C)REDQGGEWKHGR, corresponding to amino acid residues 747-758 of human neuropilin-2 (Accession O60462). Extracellular, N-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain synaptosomal fraction (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain synaptosomal fraction (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Neuropilin-2/NRP2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR062).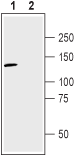 Western blot analysis of human U-87 MG glioma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human U-87 MG glioma cell line lysate:1. Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062), (1:200).
2. Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Neuropilin-2/NRP2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR062).
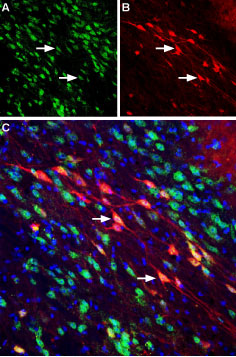 Expression of Neuropilin-2 in mouse substantia nigra pars compactaImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062), (1:400). A. NRP2 staining (green) reveals several neuronal profiles of NRP2 positive neurons that are distributed along the substantia nigra pars compacta. B. The same section stained for Calbindin-D28K (red) shows positive neurons along the substantia nigra pars compacta. C. Merge of the two images reveals co-localization in several neurons (arrows). DAPI counterstain is used to visualize nuclei of all cells (blue).
Expression of Neuropilin-2 in mouse substantia nigra pars compactaImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062), (1:400). A. NRP2 staining (green) reveals several neuronal profiles of NRP2 positive neurons that are distributed along the substantia nigra pars compacta. B. The same section stained for Calbindin-D28K (red) shows positive neurons along the substantia nigra pars compacta. C. Merge of the two images reveals co-localization in several neurons (arrows). DAPI counterstain is used to visualize nuclei of all cells (blue).
 Cell surface detection of Neuropilin-2 in live intact human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cell line:___ Unstained cells + goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-647 secondary antibody.
Cell surface detection of Neuropilin-2 in live intact human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cell line:___ Unstained cells + goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-647 secondary antibody.
___ Cells + Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062), (1:15) + goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-647 secondary antibody.
- Wild, J.R. et al. (2012) Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 93, 81.
- Prud'homme, G.J. and Glinka, Y. (2012) Oncotarget 3, 921.
- Bagri, A. et al. (2009) Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 1860.
The neuropilins (NRPs) are single-pass multifunctional transmembrane glycoproteins that play an important role in cell development, immunity and cancer, and physiological and pathological angiogenesis. They were first discovered as regulators of nervous system development, acting as semaphorin co-receptors with plexins, as well as enhancers of cellular responses to members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family.
The NRP family comprises two members: Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) and Neuropilin-2 (NRP2), which are usually expressed as homodimers but can also appear as heterodimers. NRP2 contains a large extracellular N-terminal which consists of five domains, a short transmembrane domain and a small cytoplasmic domain1-3.
NRP2 is expressed in a wide variety of cells including endothelial cells, neurons, pancreatic islet cells, hepatocytes, melanocytes and osteoblasts. NRP2 has been shown to mediate proliferation, survival, and migration of tumor cells3.
NRP2 knockout mice studies show that mice are viable without defects in blood vessels but display abnormal lymphatic development and defects of the central and peripheral nervous systems2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Neuropilin-2 (NRP2) (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-062) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and indirect flow cytometry applications. The antibody recognizes an extracellular epitope and is thus ideal for detecting the protein in living cells. It has been designed to recognize NRP2 from mouse, rat and human samples.
