Overview
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Specifications
- Peptide EQNRSADGQHAGGLVC corresponding to amino acid residues 209-224 of human NTSR1 (Accession P30989). 2nd extracellular loop.
Applications
- Various human cell lines (1:200).
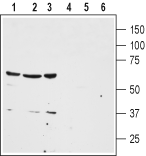 Western blot analysis of human colon cancer HT-29 (lanes 1 and 4), human lung small cell carcinoma NCI-H526 (lanes 2 and 5) and human breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB-468 (lanes 3 and 6) cell lysates:1-3. Anti-Neurotensin Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANT-015), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human colon cancer HT-29 (lanes 1 and 4), human lung small cell carcinoma NCI-H526 (lanes 2 and 5) and human breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB-468 (lanes 3 and 6) cell lysates:1-3. Anti-Neurotensin Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANT-015), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-Neurotensin Receptor 1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Neurotensin Receptor 1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT015).
- Human live MCF-7 cells (1:20).
- Human breast cancer sections (paraffin embedded) and rat brain sections (1:100).
- Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell lines (1:20).
- The control antigen is not suitable for this application.
Scientific Background
Neurotensin receptor 1 (NTR1) is one of three receptors that mediate the effects of the tridecapeptide neurotensin. Neurotensin is synthesized and secreted from neurons in the central neural system (CNS) and from endocrine cells in the gastrointestinal tract.
NTR1 and NTR2 belong to the 7-transmembrane domain, G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily while the third neurotensin receptor NTR3 (also called Sortilin) is a type I membrane protein with a large extracellular domain. Both NTR1 and NTR3 bind neurotensin with high affinity while NTR2 binds it with low affinity.1
NTR1 signals preferentially through Gaq, resulting in the activation phopholipase C and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization, although coupling with Gi/o and to Gs has been observed in some expression systems.
NTR1 is mainly expressed in the brain and gastrointestinal tract. In the brain, NTR1 mediates body temperature regulation, feeding behavior and locomotion regulation. One of the best studied roles of NTR1 is the regulation of dopamine release suggesting that NTR1 can be a suitable target for the development of a new class of anti-psychotics.2
In the periphery, NTR1 expression has been linked to the control of intestine motility and in the stimulation of growth of the intestine mucosa in both physiological and pathological conditions. NTR1 has been shown to be upregulated in several human cancers where it stimulates tumor growth in response to locally produced neurotensin peptide.3
