Overview
- Peptide (C)HREMQVSDRVRSIAKD, corresponding to amino acid residues 337-352 of rat OPRL1 (Accession P35370). Intracellular, C-terminus.

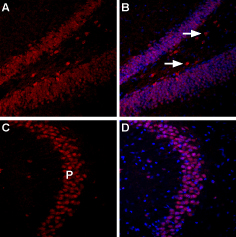 Expression of Nociceptin receptor in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of mouse hippocampus using Anti-Nociceptin Receptor (OPRL1)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AOR-015-AR), (1:60). A, B. Nociceptin receptor staining (red) in hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) appears in the outlines of neuronal cell bodies in the granule layer and in the hilus (arrows). C, D. Nociceptin receptor staining in hippocampal CA3 region appears in the outlines of neuronal cell bodies in the pyramidal layer (P). Nuclei are stained using DAPI as the counterstain.
Expression of Nociceptin receptor in mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of mouse hippocampus using Anti-Nociceptin Receptor (OPRL1)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AOR-015-AR), (1:60). A, B. Nociceptin receptor staining (red) in hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) appears in the outlines of neuronal cell bodies in the granule layer and in the hilus (arrows). C, D. Nociceptin receptor staining in hippocampal CA3 region appears in the outlines of neuronal cell bodies in the pyramidal layer (P). Nuclei are stained using DAPI as the counterstain.
- Wu, H. et al. (2012) Nature 485, 327.
- Mustazza, C. et al. (2011) Med. Res. Rev. 31, 605.
- Ruangkittisakul, A. Ballanyi, K. (2006) Neurosci. Lett. 401, 194.
- Witkin J.M. et al. (2014) Pharmacol. Ther. 141, 283.
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ), a 17 amino acid peptide, is the endogenous agonist of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) receptor (previously termed ORL1 receptor) which belongs to the class A (Rhodopsin-like) γ subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Like all members the receptor has a common seven-transmembrane helical structure and is coupled predominantly to heterotrimeric Gi/Go proteins. N/OFQ receptor shows a high degree of structural homology with the μ-, δ- and κ-opioid receptors1. The intracellular events triggered by the binding of N/OFQ with the NOP receptor include inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, activation of phospholipase C (PLC) and of K+ channels, inhibition of Ca2+ channels, and activation of mitogen-activated protein-kinases (MAPKs). In neural tissues, the main effect is the inhibition of the release of neurotransmitters (acetylcholine, catecholamines, GABA, glutamate, 5-hydroxytryptamine, tachykinines)2.
NOP receptor mRNA is detected in high levels in the cortex, anterior olfactory nucleus, lateral septum, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, central grey, pontine nuclei, interpeduncular nucleus, substantia nigra, raphe complex, locus coeruleus and spinal cord3.
Studies with N/OFQ, NOP-selective agonists or antagonists, and receptor- or peptide-deficient mice have shown that the NOP system has important roles in the control of central and peripheral functions including pain, anxiety depression, hyperphagia and obesity, addiction, Parkinson's disease, cognition, food intake, learning and memory, locomotion, cough and micturition reflexes, cardiovascular homeostasis, intestinal motility and immune responses4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Nociceptin Receptor (OPRL1) Antibody (#AOR-015) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot analysis, and has been designed to recognize the nociceptin receptor from mouse, rat and human samples.
Anti-Nociceptin Receptor (OPRL1)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AOR-015-AR) is directly labeled with an ATTO-594 fluorescent dye. ATTO dyes are characterized by strong absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield, and high photo-stability. The ATTO-594 fluorescent label belongs to the class of Rhodamine dyes and can be used with fluorescent equipment typically optimized to detect Texas Red and Alexa-594. Anti-Nociceptin Receptor (OPRL1)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody has been tested in immunohistochemistry applications and is specially suited to experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.
