Overview
- Peptide GEIKTGNSPV(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 39-48 of mature human NT-3 (residues 177-186 of the NT-3 precursor) (Accession P20783).
- 10 ng Recombinant human Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) protein (1:1000).
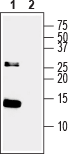 Western blot analysis of Recombinant human Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) protein (#N-260), (100 ng):1. Anti-Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) Antibody (#ANT-003), (1:200)2. Anti-Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) Antibody, preincubated with Neurotrophin 3/NT-3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT003).
Western blot analysis of Recombinant human Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) protein (#N-260), (100 ng):1. Anti-Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) Antibody (#ANT-003), (1:200)2. Anti-Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) Antibody, preincubated with Neurotrophin 3/NT-3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT003).
- Mouse spinal cord. Rat hippocampus (1:300) (Ramos Languren, L.E. and Escobar, M.L. (2013) Eur. J. Neurosci. 37, 1248).
The neurotrophins ("neuro" meaning nerve and "trophe" meaning nutrient) are a family of soluble, basic growth factors which regulate neuronal development, maintenance, survival and death in the CNS and PNS.1 The structural hallmark of all neurotrophins is the characteristic arrangement of the disulfide bridges, known as the cysteine knot, which has been found in other growth factors such as PDGF.2 The rat and human forms of neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) are 96% homologous.
NT-3 has been shown to strengthen synaptic connections to motoneurons in the neonatal rat,3 to serve as an anti-inflammatory factor, to suppress microglial activation,4 to play a critical role in regulating T helper 1/T helper 2 cell balance5 and to modify potassium currents in isolated inner hair cells from guinea pig cochlea.6 The biological effects of NT-3 are mediated by two receptors: TrkC, which is specific for NT-3, and p75NTR, which binds all the neurotrophins.7
