Overview
- Peptide (C)KFLPLKRQAGQPS, corresponding to amino acid residues 200-212 of mouse Orai1 (Accession Q8BWG9). 2nd extracellular loop.
- Rat RBL cells (1:100).
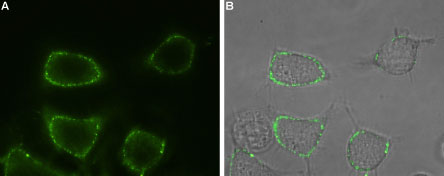 Expression of Orai1 in rat RBL cellsCell surface detection of Orai1 in intact living rat basophilic leukemia (RBL) cells using Anti-Orai1 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ACC-062-AG), (1:100). A. Extracellular staining of RBL cells (green). B. Merge of A and live view of the cells.
Expression of Orai1 in rat RBL cellsCell surface detection of Orai1 in intact living rat basophilic leukemia (RBL) cells using Anti-Orai1 (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ACC-062-AG), (1:100). A. Extracellular staining of RBL cells (green). B. Merge of A and live view of the cells.
Cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) has long been known to act as a key second messenger in many intracellular pathways including synaptic transmission, muscle contraction, hormonal secretion, cell growth and proliferation1,2. Intracellular Ca2+ levels are controlled by either the influx of Ca2+ through the calcium-release-activated Ca2+ channels (CRAC), or from intracellular stores which gained much attention.
Recently, several key players of the store operated complex have been identified3. Orai1 (also known as CRACM1) acts as the store operated Ca2+ channel (SOC) and STIM1, which acts as the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ sensor3,4. The formation of functional channels requires the presence of both Orai1 and STIM1 proteins working as a complex and involves the co-clustering of Orai1 on the plasma membrane with STIM1 on the endoplasmic reticulum4-6. TRPC1, a member of the transient receptor potential family was also suggested to act as a player in the SOC complex7. In T-cells, Ca2+ entry following activation by antigen-receptor engagement occurs solely through CRAC channels where Orai1 constitutes the pore forming subunit3,8.
Orai1 is a plasma membrane protein with four potential transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-terminus. In addition, two mammalian homologs to Orai1 have been identified; Orai2 and Orai33,9. All three, Orai1 Orai2 and Orai3, are capable of forming store operated channels with different magnitudes9.
