Overview
- Peptide (C)REFVHRGYLDLMGAS, corresponding to amino acid residues 28-42 of rat Orai3 (Accession Q6AXR8). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat and mouse heart membranes (1:800-1:2500).
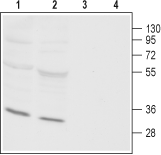 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) heart membranes:1,2. Anti-Orai3 Antibody (#ACC-065), (1:800).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) heart membranes:1,2. Anti-Orai3 Antibody (#ACC-065), (1:800).
3,4. Anti-Orai3 Antibody, preincubated with Orai3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC065).
In non-excitable cells, Ca2+ signaling plays a most important role in important cellular functions such as migration, proliferation and differentiation1. In such cells, Ca2+ enters via either non-selective cation channels such as TRPCs or through highly selective Ca2+ such as Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channels (CRAC channels) or store-operated Ca2+ entry channels (SOC channels), and the arachidonic acid-regulated Ca2+ channels (ARC channels)2.
Orai channels are part of the molecular components involved in the Ca2+ entry described above. Three Orai channels have been described in mammalian cells: Orai1-3. These channels make up the pore forming unit of CRAC channels3. They are membrane proteins with four transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini. Orai1 and Orai3 share similar distribution and are expressed in the heart, brain, liver, spleen, lung, intestine, lymphoid organs, skin, and skeletal muscle. Expression of Orai2 is more limited and is found mainly in the brain and lower expression is detected in the lung, spleen and intestine3.
CRAC channels have been for the most part identified as homotetramers of Orai1 interacting with endoplasmic reticulum located STIM1 that are activated by a depletion of intracellular Ca2+ 4. Orai3 was shown to emit store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) currents along with STIM1/2 in breast cancer cells which are Estrogen Receptor positive (ER+), whereas Orai1/STIM1 are responsible for these currents in Estrogen Receptor negative (ER-) cells1. Furthermore, inhibition of Orai3 in these cells elicits cell cycle arrest and ultimately apoptosis (normal cells do not undergo apoptosis)5. ARC channels are composed of a heteropentameric organization of Orai1/Orai3 (in a 3:2 ratio) which interacts with the small fraction of plasma membrane localized STIM1. These channels are activated by low concentrations of arachidonic acid localized at the inner face of the plasma membrane6.
