Overview
- Peptide (CS)DPVATSSTLGLQENMRTS, corresponding to amino acid residues 382-399 of rat P2X1 receptor (Accession P47824). Intracellular, C-terminus.
- Human platelets (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of human platelet lysates:1. Anti-P2X1 Receptor Antibody (#APR-001), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human platelet lysates:1. Anti-P2X1 Receptor Antibody (#APR-001), (1:200).
2. Anti-P2X1 Receptor Antibody, preincubated with P2X1 Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR001).
- HEK-293 transfected cells (Agboh, K.C. et al. (2009) Neuropharmacology 56, 230.).
- Rat supra-optic nucleus in axonal processes and heart paraffin section.
Mouse mesenteric arteries (Vial, C. and Evans, R.J. (2002) Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 1438.).
- Human Jurkat and CD4+ T cells (Woerhle, T. et al. (2010) Blood 116, 3475.).
- Human skin-resident T cells (MacLeod, A.S. et al. (2014) J. Immunol. 192, 5695.).
The P2X receptors belong to the ligand-gated ion channel family and are activated by extracellular ATP.
The structure and function of the P2X receptors, investigated mainly using in vitro models, indicate their involvement in synaptic communication, cell death, and differentiation.
Seven mammalian P2X receptor subtypes (P2X1–P2X7) have been identified and cloned.1,2,3 All P2X receptor subtypes share the same structure of intracellular N and C-termini two membrane-spanning domains and a large extracellular loop.
All P2X receptor subtypes can assemble to form homomeric or heteromeric functional channels with the exception of P2X6, which only seems to function as part of a heteromeric complex.4-9
The various P2X receptor subtypes show distinct expression patterns. P2X1-6 have been found in the central and peripheral nervous system, while the P2X7 receptor is predominantly found in cells of the immune system.4 The P2X1 receptor is present in smooth muscle, cerebellum, dorsal horn spinal neurons, and platelets where it is suggested to play a regulatory role during in vivo homeostasis and thrombosis.3,4,10,11
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
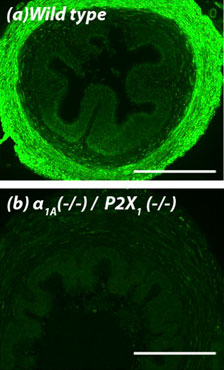 Knockout validation of Anti-P2X1 Receptor Antibody in mouse vas deferens.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse vas deferens using Anti-P2X1 Receptor Antibody (#APR-001). A. P2X1 receptor staining (green) is detected in the smooth muscle layer of wild-type vas deferens. B. In double α1A-adrenoceptor and P2X1 receptor knockout mice, there is no detection of P2X1 receptor.Adapted from White, C.W. et al. (2013) with permission of the National Academy of Sciences, USA.
Knockout validation of Anti-P2X1 Receptor Antibody in mouse vas deferens.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse vas deferens using Anti-P2X1 Receptor Antibody (#APR-001). A. P2X1 receptor staining (green) is detected in the smooth muscle layer of wild-type vas deferens. B. In double α1A-adrenoceptor and P2X1 receptor knockout mice, there is no detection of P2X1 receptor.Adapted from White, C.W. et al. (2013) with permission of the National Academy of Sciences, USA.