Overview
- Peptide (C)VEKQSTDSGAYSIGH, corresponding to amino acid residues 383-397 of rat P2X3 receptor (Accession P49654). Intracellular, C-terminus.
- Rat DRG lysates (1:200-1:500).
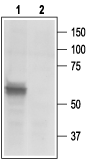 Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysates:1. Anti-P2X3 Receptor Antibody (APR-016), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat DRG lysates:1. Anti-P2X3 Receptor Antibody (APR-016), (1:200).
2. Anti-P2X3 Receptor Antibody, preincubated with P2X3 Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR016).
- Rat embryo DRG formalin frozen sections.
- Fixed mouse trigeminal neurons (1:200) (D'Arco, M. et al. (2007) J. Neurosci. 27, 8190.).
- Human CD4+ and ckit+ cells (Kazakova, R.R. et al. (2011) Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 151, 33.).
The P2X3 receptor belongs to the ligand-gated ion channel P2X receptor family, that consists of seven receptor subtypes named P2X1-P2X7 and is activated by extracellular ATP.1,2,3
All P2X subunits, with the exception of P2X6, can assemble to form homomeric or heteromeric functional channels.4-5 The different P2X receptors show distinct expression patterns. P2X1-6 has been found in the central and peripheral nervous system, while the P2X7 receptor is predominantly found in cells of the immune system. The P2X3 receptor is highly expressed on nociceptive sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) as a homomer or as a heteromer (P2X3/P2X2). ATP released from damaged cells activates the P2X3 receptor to initiate nociceptive signals.6,7 Involvement of ATP in the mechanism of chronic pain has been also suggested.7,8 P2X3 receptor is now becoming a possible target for the development of pain therapeutics.
