Overview
- Peptide (C)TRYGKELSMVKIPSK, corresponding to amino acid residues 368-382 of rat ASIC1 (Accession P55926), amino acid residues 367–381 of rat ASIC2 (Accession Q62962), amino acid residues 375–388 of rat ASIC3 (Accession O35240) and amino acid residues 378–390 of rat ASIC4 (Accession Q9JHS6). Extracellular loop.
ASIC2: Mouse, rat, human – 14/15 amino acid residues identical.
ASIC3: Mouse, rat, human – 12/15 amino acid residues identical.
ASIC4: Mouse, rat – 12/15 amino acid residues identical; human – 11/15 amino acid residues identical.
 Western blot analysis of rat dorsal root ganglion lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of rat dorsal root ganglion lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:500).
3-4. Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Pan ASIC (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SC031). Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:500).
3-4. Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Pan ASIC (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SC031).
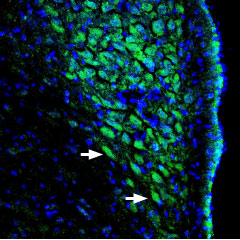 Expression of ASIC channels in rat locus coeruleusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed rat brain frozen sections using Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:400), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. ASIC channel staining (green) appears in neuronal soma (arrows). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of ASIC channels in rat locus coeruleusImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed rat brain frozen sections using Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:400), followed by goat-anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. ASIC channel staining (green) appears in neuronal soma (arrows). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
 Expression of ASIC in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of ASIC in live intact rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells with Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:25), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). B. Live view of the cells. C. Merge of A and B.
Expression of ASIC in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of ASIC in live intact rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells with Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031), (1:25), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). B. Live view of the cells. C. Merge of A and B.
- Poirot, O. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 38448.
- Krishtal, O. (2003) Trends. Neurosci. 26, 477.
- Brockway, L.M. et al. (2002) Am. J. Physiol. 283, C126.
- Ishibashi, K. et al. (1998) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 245, 589.
- Voilley, N. et al. (2001) J. Neurosci. 21, 8026.
- Wemmie, J.A. et al. (2002) Neuron 34, 463.
- Price, M.P. et al. (2000) Nature 407, 1007.
ASIC channels belong to the ENaC/Degenerin superfamily and are proton-gated ion channels which are not voltage-dependent. Six different genes encode the different ASIC subunits and splice variants: ASIC1a, ASIC1b, ASIC2a, ASIC2b, ASIC3 and ASIC4.
ASIC channels sense protons and interact with proteins (namely proteases) and other ions such as Zn2+ and Ca2+ through their extracellular domains. The extracellular loop of ASIC1a undergoes cleavage by extracellular trypsin (a serine protease) which is responsible for shifting the pH dependence of the channel activation and inactivation to more acidic pH1.
These channels are expressed in the brain and in the nervous system2 but have also been found in the retina, testes, and other tissues3,4 where they are involved in many physiological processes including nociception5, learning and memory6, mechanosensation7 among others.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer an antibody directed against an epitope of rat ASIC1. The antibody recognizes ASIC1 through ASIC4. Anti-pan ASIC (extracellular) Antibody (#ASC-031) can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry in living cells. It has been designed to recognize all ASIC channels from rat, human and mouse samples.

