Overview
- Peptide (C)HLRGQRWPFGEAA(S)R, corresponding to amino acid residues 136-150 of human PAR4 (Accession Q96RI0). Cys 149 was replaced with Ser. 1st extracellular loop.
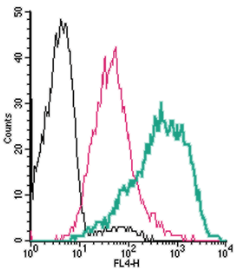 Cell surface detection of PAR4 by direct flow cytometry in live intact human MEG-01 megakaryocytic cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of PAR4 by direct flow cytometry in live intact human MEG-01 megakaryocytic cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG isotype control-APC.
___ Cells + Anti-PAR4 (F2RL3) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#APR-034-APC), (2.5µg). Cell surface detection of PAR4 by direct flow cytometry in live intact mouse P815 mast cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of PAR4 by direct flow cytometry in live intact mouse P815 mast cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + Rabbit IgG isotype control-APC.
___ Cells + Anti-PAR4 (F2RL3) (extracellular)-APC Antibody (#APR-034-APC), (2.5µg).
Protease-activated receptor 4 (PAR-4) belongs to a family of four G protein-coupled receptors (PAR1-4) that are activated as a result of proteolytic cleavage by certain serine proteases, hence their name. In this novel modality of activation, a specific protease cleaves the PAR receptor within a defined sequence in its extracellular N-terminal domain. This results in the creation of a new N-terminal tethered ligand, which subsequently binds to a site in the second extracellular loop of the same receptor. This binding results in the coupling of the receptor to G proteins and in the activation of several signal transduction pathways.1-3
Different PARs are activated by different proteases. Hence, PAR-4 is activated by both thrombin and trypsin whereas PAR-1 and PAR-3 are activated only by thrombin and PAR-2 is activated only by trypsin.1-3 PAR-4 can be also cleaved and activated by other proteases such as cathepsin G.
The intracellular signaling mechanisms mediated by PAR-4 activation are not completely elucidated but they involve calcium mobilization downstream of phospholipase Cβ through the Gαq pathway.1-3
Tissue distribution of PAR-4 is very broad with the highest expression levels found in lung, testis, pancreas and small intestine. In addition, PAR-4 expression was observed in platelets, megakaryocytes and leukocytes. Studies with platelets derived from PAR-4 knockout mice have established an essential role for PAR-4 in thrombin-induced platelet activation.
PAR-4 is likely involved in other physiological functions such as regulation of gastrointestinal motility and regulation of vascular endothelial cell function.1-3
