Overview
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Specifications
- Peptide (C)RKLTKNSEADGMFAY, corresponding to amino acid residues 201 - 215 of mouse Plexin-A4 (Accession Q80UG2). Extracellular, N-term.
Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR084)
Applications
 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-084), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1-2. Anti-Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-084), (1:200).
3-4. Anti-Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-PR084).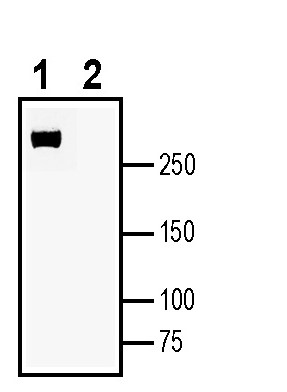 Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate:1. Anti-Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-084), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate:1. Anti-Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-084), (1:200).
2. Anti-Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Plexin-A4 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (BLP-PR084).
Scientific Background
The plexin family are transmembrane proteins which are classified into four subfamilies: plexin -A, B, C and D. The plexins serve as a receptor for seamaphorins (Sema), axon guidance molecules involved in cellular processes such as axon pruning and repulsion, regulation of cell migration, vascular remodeling and more1.
All family members consist of a Sema domain at the N-terminus responsible for Sema binding. In addition, plexins have PSI and IPT (Integrin, Plexin, and Transcription factor) domains, which connect to the transmembrane (TM) helix. Moreover, intracellular region of all plexins contains a membrane proximal juxtamembrane region (JM), a Rho GTPase-binding domain (RBD), and GTPase Activating Protein (GAP) domain2.
Plexin-A4 acts as a receptor for the secreted semaphorins Sema3A and Sema6A in the central nervous system, and mediates axon repulsion and synaptic plasticity. Moreover, genome-wide significant association study (GWAS) on humans, has identified that several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in PLXNA4 can increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) 3,4.
In the immune system, Plexin-A4 has been implicated in macrophage Toll-like receptor (TLR)–mediated signaling in sepsis, negative regulation of T-cell mediated immune responses in cancer5.
