Overview
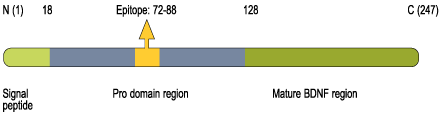
- Peptide (C)DEDQKVRPNEENNKDAD, corresponding to amino acid residues 72-88 of human BDNF (precursor) (Accession P23560). Prodomain of the BDNF protein.
- Human isolated platelets (Azoulay, D. et al. (2014) Br. J. Haematol. 164, 451.).
- Lee R. et al. (2001) Science 294, 1945.
- Egan, M.F. et al. (2003) Cell 112, 257.
- Pang, P.T. et al. (2004) Science 306, 487.
- Michalski, B. et al. (2003) Mol. Brain Res. 111, 148
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors that includes nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5).
All neurotrophins are synthesized as preproneurotrophin precursors that are subsequently processed within the intracellular transport pathway to yield proneurotrophins that are further processed to generate the mature form. The mature form of BDNF is a non-covalent stable homodimer that can be secreted in both constitutive and regulated pathways.
Until recently, the functional role of the neurotrophin prodomains were thought to include assistance in the correct folding of the mature protein and the sorting of the neurotrophins into the constitutive or regulated secretory pathway. However, a growing body of evidence suggests that the uncleaved proneurotrophin precursors can be secreted from cells and that they may mediate different biological functions.
The functional importance of the prodomain of BDNF was recently demonstrated in a study showing that a polymorphism that replaces valine for methionine at position 66 of the prodomain, is associated with memory defects and abnormal hippocampal function in humans. Another recent study showed that the regulated extracellular cleavage of proBDNF to mature BDNF by plasmin is necessary for establishing late-phase long-term potentiation (L-LTP), a process that involves long-lasting changes in the structure and function of hippocampal synapses. Finally, proBDNF was shown to be decreased in the brains of patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease.
Mature BDNF binds to the specific tyrosine kinase receptor TrkB and to p75NTR, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily. proBDNF can similarly bind both receptors although it appears to have a greater affinity for the p75NTR receptor.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-proBDNF Antibody (#ANT-006) is a highly specific antibody directed against the prodomain region of human proBDNF. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize proBDNF from human, mouse, and rat samples. The antibody does not cross react with mature BDNF, pro- and mature NGF or mature NT-3.
Anti-proBDNF-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#ANT-006-AG) is directly labeled with an ATTO-488 fluorescent dye. ATTO dyes are characterized by strong absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield, and high photo-stability. The ATTO-488 label is analogous to the well known dye fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and can be used with filters typically used to detect FITC. Anti-proBDNF-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody is especially suited for experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.
Applications
Citations
- Human isolated platelets.
Azoulay, D. et al. (2014) Br. J. Haematol. 164, 451.

