Overview
- Peptide (C)RAPHWYASHMKTR, corresponding to amino acid residues 137-149 of mouse prostanoid EP3 receptor (Accession P34980). 2nd intracellular loop.
- Mouse and rat kidney membranes, rat pancreas membranes and human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell lysate (1:200-1:2000).
 Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and pancreas (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody (#APR-065), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat kidney (lanes 1 and 3) and pancreas (lanes 2 and 4) membranes:1,2. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody (#APR-065), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody, preincubated with Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3/PTGER3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR065). Western blot analysis of mouse kidney membranes:1. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody (#APR-065), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse kidney membranes:1. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody (#APR-065), (1:200).
2. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody, preincubated with Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3/PTGER3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR065).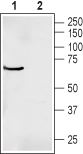 Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell lysate:1. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody (#APR-065), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell lysate:1. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody (#APR-065), (1:400).
2. Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody, preincubated with Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3/PTGER3 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR065).
- Human blood eosinophils (Durchschein, F. et al. (2019) Dig. Dis. Sci. 64, 2806.).
Prostaglandin is a small molecule produced from arachidonic acid by the enzymes COX1, COX2 and PG synthase. PGE2 regulates various factors of inflammatory response, promoting local vasodilatation and attracting immune system cells to the site of the inflammation.
Prostanoid EP3 receptor, a member of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily, is one of four PGE2 receptors (EP1-EP4) and binds PGE2 with a higher affinity than other receptors of its class. Unlike EP2 and EP4, EP3 is not coupled to Gs and lacks cAMP activating functions. In contrast, most of its splice variants couple with Gi and inhibit adenylate cyclase activity1. EP3 binds prostaglandin in a GTP dependent manner. One of the receptor’s extracellular domains, ECII, can alter GTP effect on agonist binding and thus the receptor’s downstream intracellular signaling. ECII causes receptor conformational changes2.
EP3 plays a role in pulmonary hypertension (PAH) pathophysiology. It is hypothesized that EP3 levels are upregulated in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells and in human distal pulmonary arteries in response to hypoxia. Blocking agents for the EP3 receptor may prove as a useful strategy in the treatment of PAH3.
EP3 is also involved in the cell growth, invasion and migration of many tumor types including bladder cancer. EP3 has been found to be significantly less expressed in muscular and non-muscular invasive bladder cells than in normal urothelial cells4.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
EP3 receptor expression increases in LPS-treated astrocytes.Western blot analysis of rat primary astrocyte using Anti-Prostaglandin E Receptor EP3 (PTGER3) Antibody (#APR-065). EP3 receptor expression increases following LPS stimulation (right lane).Adapted from Paniagua-Herranz, L. et al. (2017) Front. Pharmacol. 8, 937. with permission of Frontiers.
