Overview
- Peptide (C)TQAIAPDSREMGD, corresponding to amino acid residues 290-302 of rat PTGIR (Accession P43253). Extracellular, 3rd loop.
- Rat lung membranes, mouse heart and lung membranes and human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell, THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell, and MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cell lysates (1:200-1:2000).
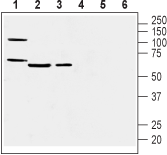 Western blot analysis of mouse heart membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse lung lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and rat lung membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Prostacyclin Receptor (PTGIR) (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-068), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of mouse heart membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse lung lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and rat lung membranes (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Prostacyclin Receptor (PTGIR) (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-068), (1:400).
4-6. Anti-Prostacyclin Receptor (PTGIR) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Prostacyclin Receptor/PTGIR (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR068). Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell (lanes 1 and 4), human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell (lanes 2 and 5) and human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cell (lanes 3 and 6) lysates:1-3. Anti-Prostacyclin Receptor (PTGIR) (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-068), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human Jurkat T-cell leukemia cell (lanes 1 and 4), human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell (lanes 2 and 5) and human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cell (lanes 3 and 6) lysates:1-3. Anti-Prostacyclin Receptor (PTGIR) (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-068), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-Prostacyclin Receptor (PTGIR) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Prostacyclin Receptor/PTGIR (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PR068).
- Human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cells (1:20).
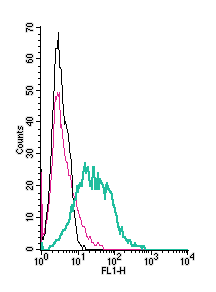 Cell surface detection of PTGIR by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of PTGIR by indirect flow cytometry in live intact human MEG-01 megakaryoblastic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-Prostacyclin Receptor (PTGIR) (extracellular) Antibody (#APR-068), (5μg) + goat-anti-rabbit-FITC.
Prostaglandins comprise a family of locally acting hormones, whose synthesis is initiated by the enzyme COX. This pathway is involved in a broad variety of pathological conditions such as cancer, inflammation and hypertension.
Prostaglandin I2 receptor (PGI2 receptor) is G-coupled protein receptor (GPCR) with seven hydrophobic transmembrane segments and an extracellular NH2 terminus. Prostaglandin receptors belong to family A, group V of GPCRs. There is significant ligand-binding cross-reactivity between different prostaglandins and different receptors in the family. Within the PG family, receptors share roughly 20-30% of their sequence and there are 34 identical residues across the family. Twenty of these residues are unique to PG receptors and are not shared by other GPCRs. The unique residues reside mostly in the transmembrane region and in the second extracellular loop region. Both of these regions are implicated in ligand binding. The PGI2 receptor signals primarily via stimulation of cAMP generation but through PIP2 as well despite a much higher agonist concentration required for PIP2 hydrolysis.
PGI2 receptor mRNA is highly expressed in the human heart, aorta, kidney, liver and lung tissues and in mice thymus, heart and spleen1. Mice lacking PGI2 receptor have been shown to have a reduced inflammation response and a significant decrease in clinical arthritis. In addition, human patients with a dysfunctional PGI2 receptor variant exhibit an enhanced atherothrombotic phenotype with higher incidence of triple vessel coronary disease and cardiovascular events2.
