Overview
- Peptide (C)KDWGSSSGSQGRED, corresponding to amino acid residues 505-518 of human PSD-95 (Accession P78352). Intracellular, between the SH3 and the GK-like domains.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain synaptosomal fraction (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-PSD-95 Antibody (#APZ-009), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain synaptosomal fraction (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-PSD-95 Antibody (#APZ-009), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-PSD-95 Antibody, preincubated with PSD-95 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PZ009).
 Expression of PSD-95 in mouse parietal cortexImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-PSD-95 Antibody (#APZ-009), (1:400), followed by anti-rabbit-Cy3 antibody (red). Staining appears mainly in the pyramidal cell body (arrows). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of PSD-95 in mouse parietal cortexImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Anti-PSD-95 Antibody (#APZ-009), (1:400), followed by anti-rabbit-Cy3 antibody (red). Staining appears mainly in the pyramidal cell body (arrows). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
- Feng, W. and Zhang, M. (2009) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 87.
- Scannevin, R.L. and Huganir, R.L. (2000) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 1, 133.
- Doucet, M.V. et al. (2012) Pharmacol. Ther. 133, 218.
- Kalia, L.V. and Salter, M.W. (2003) Neuropharmacology 45, 720.
- Carlisle, H.J. et al. (2008) J. Physiol. (Lond.) 586, 5885.
The postsynaptic density (PSD) is a membrane-associated protein specialized in postsynaptic signal transduction and processing. There are four PSD family members classified according to their molecular weight, including, PSD-95, PSD-93, synaptic associated proteins 97 kDa and 102 kDa. PSD-95 interacts with both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors via protein–protein interactions and plays a role in their precise assembly and spatial organization as well as coupling of these receptors to downstream signaling events1.
PSD-95 contains a SH3 domain, a GK domain and three PDZ domains. The PDZ domains 1 and 2 of PSD-95 are separated by only a few residues, creating a rigid bond that may restrain interdomain flexibility. These two PDZ domains can have distinct or overlapping target-binding proteins. In contrast, PDZ3 of PSD-95 is located at the carboxyl terminal end of the protein and has a set of interacting proteins that are distinct from PDZ domains 1 and 2. The N-palmitoylation of PSD-95 at Cys-3 and Cys-5 residues is essential for enhanced synaptic responses and the trafficking of PSD-95 to the plasma membrane2. With its numerous domains, PSD-95 is often referred to as a scaffold protein, which localizes and traffics various receptors, cell adhesion molecules, ion channels, kinases and phosphatases to the synaptic membrane. PSD-95 also interacts with a variety of adaptor and cytoskeleton proteins, molecular motors, as well as protein synthesis machinery3.
PSD-95 is found at the postsynaptic membrane of excitatory synapses4.
PSD-95 null mice have severe learning defects and exhibit both facilitation of long-term potentiation and disruption of long-term depression5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope human PSD-95. Anti-PSD-95 Antibody (#APZ-009) can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize PSD-95 from mouse, rat and human samples.
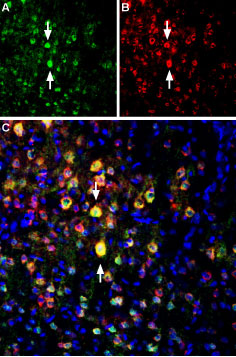
Multiplex staining of PSD-95 and GluN2B in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat parietal cortex sections using Anti-PSD-95 Antibody (#APZ-009), (1:400) and Anti-NMDAR2B (GluN2B) (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#AGC-003-AR), (1:60). A. PSD-95 staining (green). B. The same sections were stained for GluN2B (red). C. Merge of the two images shows several cells expressing both proteins (arrows point to several examples). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Applications
Citations
- Mouse sample:
Bodaleo, F.J. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 30069.
- Mouse sample:
Jones, B.W. et al. (2016) eLife. 5, e20695.
