Overview
- Peptide CRDPDYGTLIQE, corresponding to amino acid residues 27-38 of rat RAMP1 (Accession Q9JJ74). Extracellular, N-terminus.

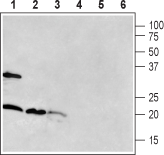 Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain (lanes 2 and 5) and rat pancreas (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-RAMP1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ARR-021).
Western blot analysis of rat brain (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain (lanes 2 and 5) and rat pancreas (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-RAMP1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ARR-021).
4-6. Anti-RAMP1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with RAMP1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-RR021).
The antibody was used at a concentration of 1:400 for brain lysates and 1:200 for pancreas lysates.
 Expression of RAMP1 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat free-floating frozen section using Anti-RAMP1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ARR-021). A. In the parietal cortex, RAMP1 immunoreactivity (green) appears in pyramidal neurons (arrows). B. In the hippocampus, RAMP1 staining (green) is detected in the CA1 region (arrows). Nuclei are demonstrated using DAPI as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of RAMP1 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat free-floating frozen section using Anti-RAMP1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ARR-021). A. In the parietal cortex, RAMP1 immunoreactivity (green) appears in pyramidal neurons (arrows). B. In the hippocampus, RAMP1 staining (green) is detected in the CA1 region (arrows). Nuclei are demonstrated using DAPI as the counterstain (blue).
- Kadmiel, M. et al. (2012) Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 744, 49.
- Jacob, A. et al. (2012) Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 744, 87.
- Conner, A.C. et al. (2004) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 32, 843.
- Li, M. et al. (2014) PLoS One 9, e102356.
- Shi, B. et al. (2014) Exp. Biol. Med. 239, 356.
Receptor activity modifying protein-1 (RAMP1) is part of a three-member group (that further includes RAMP2 and RAMP3 – each encoded by a different gene) of transmembrane proteins that interact with G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) such as the calcitonin receptor-like receptors (CLRs)1. This interaction leads to the formation of the receptor for calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) and is necessary for the binding of the peptide to the receptor. The binding of RAMP2 and RAMP3 to CLR, on the other hand, creates the receptor for adrenomedullin, a peptide functionally and structurally related to calcitonin1,2.
RAMP1 (as well as the two other RAMPs) has a short intracellular domain and a single transmembrane domain. Its extracellular region contains four conserved cysteine residues that putatively form two disulfide bonds. This domain confers specificity to the receptor complex, whereas the transmembrane chain allows the association of the RAMPs with the GPCRs. In contrast to the other RAMPs, RAMP1 lacks glycosylation sites and therefore is unable to migrate to the cell surface independently. To reach the cell surface, it aggregates inside the cytoplasm and forms heterodimers with calcitonin3.
RAMP1 is highly prominent in the neuronal tissues (especially the trigeminal ganglion, striatum, cortex, olfactory bulb, dorsal root ganglion, and the spinal cord) but abundant as well in the electrical conducting system of the heart, blood vessels, and related sites1,2,4.
While not dramatically affected, RAMP1-KO mice are reported to have higher blood pressure and to suffer from repressed wound healing process, while overexpression of RAMP1 in animals leads to extravasation and vasodilation2. Interestingly, asthmatic symptoms in mice model of asthma were mitigated in mice that were RAMP1-deficient4. Furthermore mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing RAMP1 were shown to improve cardiac function and to reduce occurrences of over-thickened blood vessels5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti–RAMP1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ARR-021) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and live cell imaging applications. It has been designed to recognize RAMP1 from rat and mouse samples. The antibody does not recognize RAMP1 from human samples.