Overview
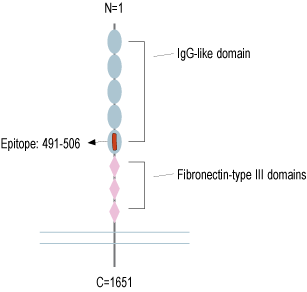
- Peptide (C)DGVLVSTQDSRIKQLE, corresponding to amino acid residues 491 - 506 of human Robo1 (Accession Q9Y6N7). Extracellular, N-term.
 Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-181), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain membranes (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-181), (1:200).
3, 4. Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Robo1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR181) (#BLP-NR181). Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), human MDA-MB-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-181), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line lysate (lanes 1 and 4), human MDA-MB-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell line lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-181), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Robo1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR181) (#BLP-NR181).
 Expression of Robo1 in mouse cortexImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-181), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Robo1 immunoreactivity (green) appears in neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Robo1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR181), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of Robo1 in mouse cortexImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-181), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Robo1 immunoreactivity (green) appears in neurons (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Robo1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR181), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Jiang, Z. et al. (2019) Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 11, 1.
- Blockus, H. and Chedotal, A. (2016) Development 143, 3037.
- Li, H.S. et al. (1999) Cell 96, 807.
- Carr, L. et al. (2017) PLoS One 12, e0172736.
- Chedotal, A. (2007) Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 621, 65.
- Su, X. et al. (2016) Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 38, 70.
Roundabout (Robo) receptors are a conserved family of four single pass transmembrane proteins1. All members have multiple immunoglobulin-like domains in the extracellular N-terminal region, three extracellular fibronectin type II domains, and cytoplasmic conserved domains. Robos also undergo preoteolytic processing, important for their signaling process2. They serve as receptors for Slit proteins, where upon activation lead to pleiotropic effects including axonal guidance1, axonal repulsion3,4, and neural migration5.
Slit/Robo signaling mainly prevents axons from migrating to inappropriate locations during the assembly of the nervous system6.
Robos are mainly expressed in the nervous system, but are also detected in vascular endothelial and muscle cells7. In non-neuronal tissues, Slit/Robo proteins are key oncogenes and tumor suppressors in various types of cancers. Robo1 expression is elevated in breast cancer and colorectal cancer, and has an overall oncogenic role1.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Robo1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ANR-181) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and live cell flow cytometry. It has been designed to recognize Robo1 from human, rat, and mouse samples.

