Overview
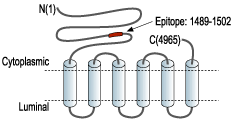
- Peptide CAGESMSPGQGRNN, corresponding to amino acid residues 1489-1502 of human RyR2 (Accession Q92736). Intracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:200).
2. Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody, preincubated with Ryanodine Receptor 2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-RR002).
 Expression of RyR2 in rat cardiac muscleImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded sections of rat myocardium using Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:50). Staining is specific for cardiomyocytes while smooth muscles cells in the artery walls are negative (red arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of RyR2 in rat cardiac muscleImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded sections of rat myocardium using Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:50). Staining is specific for cardiomyocytes while smooth muscles cells in the artery walls are negative (red arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain. Expression of RyR2 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum frozen sections with Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:100), (green fluorescence). A. The highest expression of RyR2 is in the molecular layer (asterisk) but there is also some expression in the soma of Purkinje cells (arrows). B. In the same section, there is staining for parvalbumin (red), a marker for Purkinje cells. C. Merged image of panels A and B demonstrates that RyR2 is localized both in the area surrounding the dendritic tree and in the soma of Purkinje cells. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of RyR2 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum frozen sections with Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:100), (green fluorescence). A. The highest expression of RyR2 is in the molecular layer (asterisk) but there is also some expression in the soma of Purkinje cells (arrows). B. In the same section, there is staining for parvalbumin (red), a marker for Purkinje cells. C. Merged image of panels A and B demonstrates that RyR2 is localized both in the area surrounding the dendritic tree and in the soma of Purkinje cells. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
- Mouse primary hippocampal neurons (1:300) (Gan, K.J. and Silverman, M.A. (2015) Mol. Biol. Cell 26, 1058.)
- Chakrabarti, R. and Chakrabarti, R. (2006) J. Cell. Biochem. 99, 1503.
- Eisner, D.A. et al. (2005) Exp. Physiol. 90, 3.
- Bers, D.M. (2004) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 37, 417.
- Fill, M. and Copello, J.A. (2002) Physiol. Rev. 82, 893.
It is well established that cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) acts as a key second messenger in many intracellular pathways including synaptic transmission, muscle contraction, hormonal secretion, cell growth and proliferation.1,2 The primary intracellular Ca2+ storage/release organelle in most cells is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) in striated muscle cells.
The ER and SR contain two Ca2+ release channel families, the inositol trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) and the ryanodine receptors (RyRs).3
The ryanodine receptor family consists of three different isoforms: the skeletal muscle isoform, ryanodine receptor type 1 (RyR1); the cardiac muscle isoform, ryanodine receptor type 2 (RyR2) and the brain isoform, ryanodine receptor type 3 (RyR3).3
The ryanodine receptors are homotetrameric proteins, which upon assembly create a Ca2+ conducting channel. They play a key role in the mechanism of excitation-contraction coupling in striated muscle. Binding of ryanodine (a poisonous alkaloid found in the South American plant Ryania speciosa) to the ryanodine receptor causes two major changes in the channel: a reduction in single-channel conductance and a marked increase in the open state probability, leading to an overall increase/decrease in the Ca2+ release capability of the channel.
RyR2 serves as an intracellular Ca2+ channel in the SR membrane. It is predominantly expressed in cardiac muscle where it plays a central role in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. RyR2 is also expressed in the brain.1-4
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of human RyR2. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize RyR2 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
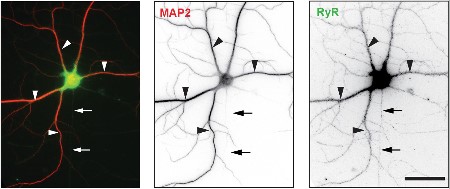
Expression of RyR2 in mouse hippocampal neurons.Immunocytochemical staining of mouse primary hippocampal neurons using Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002).Adapted from Gan, K.J. and Silverman, M.A. (2015) Mol. Biol. Cell 26, 1058. with permission of the American Society for Cell Biology.
Applications
Citations
- Rat heart sections (1:50).
Zhu-Mauldin, X. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 39094. - Rat tibialis anterior muscle sections (1:100).
Kraner, S.D. et al. (2011) Am. J. Physiol. 300, R1384.
- Mouse isolated vascular smooth muscle cells.
Thakore, P. et al. (2020) Sci. Signal. 13, eaba1015. - Rat adipose-derived stromal cells and rat bone marrow stromal cells.
Forostyak, O. et al. (2016) Stem Cell Res. 16, 622. - Mouse primary hippocampal neurons (1:300).
Gan, K.J. and Silverman, M.A. (2015) Mol. Biol. Cell 26, 1058.
- Yoshida, S. et al. (2010) Neurosci. Res. 68, 322.
