Overview
- Peptide CAGESMSPGQGRNN, corresponding to amino acid residues 1489-1502 of human RyR2 (Accession Q92736). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat heart membrane (1:200). The addition of 0.1% Tween-20 to the blocking and primary antibody solutions is recommended.
 Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat heart membranes:1. Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002), (1:200).
2. Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody, preincubated with Ryanodine Receptor 2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-RR002).
- Mouse cerebellum frozen section and in rat heart paraffin embedded section (1:100).
- Mouse primary hippocampal neurons (1:300) (Gan, K.J. and Silverman, M.A. (2015) Mol. Biol. Cell 26, 1058.)
It is well established that cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) acts as a key second messenger in many intracellular pathways including synaptic transmission, muscle contraction, hormonal secretion, cell growth and proliferation.1,2 The primary intracellular Ca2+ storage/release organelle in most cells is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) in striated muscle cells.
The ER and SR contain two Ca2+ release channel families, the inositol trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) and the ryanodine receptors (RyRs).3
The ryanodine receptor family consists of three different isoforms: the skeletal muscle isoform, ryanodine receptor type 1 (RyR1); the cardiac muscle isoform, ryanodine receptor type 2 (RyR2) and the brain isoform, ryanodine receptor type 3 (RyR3).3
The ryanodine receptors are homotetrameric proteins, which upon assembly create a Ca2+ conducting channel. They play a key role in the mechanism of excitation-contraction coupling in striated muscle. Binding of ryanodine (a poisonous alkaloid found in the South American plant Ryania speciosa) to the ryanodine receptor causes two major changes in the channel: a reduction in single-channel conductance and a marked increase in the open state probability, leading to an overall increase/decrease in the Ca2+ release capability of the channel.
RyR2 serves as an intracellular Ca2+ channel in the SR membrane. It is predominantly expressed in cardiac muscle where it plays a central role in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. RyR2 is also expressed in the brain.1-4
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
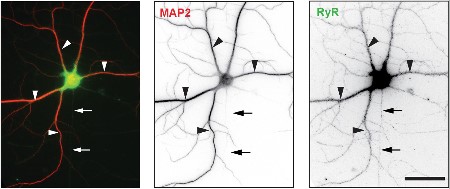
Expression of RyR2 in mouse hippocampal neurons.Immunocytochemical staining of mouse primary hippocampal neurons using Anti-Ryanodine Receptor 2 Antibody (#ARR-002).Adapted from Gan, K.J. and Silverman, M.A. (2015) Mol. Biol. Cell 26, 1058. with permission of the American Society for Cell Biology.
