Overview
- Peptide (C)KRDRKQRRQRPGH, corresponding to amino acid residues 728-740 of rat SEMA3A (Accession Q63548). C-terminus.
- Rat and mouse brain lysates. Human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia and MDA-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysates (1:400-1:1200).
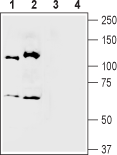 Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-Semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) Antibody (#ASR-051), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of mouse (lanes 1 and 3) and rat (lanes 2 and 4) brain membranes:1,2. Anti-Semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) Antibody (#ASR-051), (1:400).
3,4. Anti-Semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) Antibody, preincubated with Semaphorin 3A/SEMA3A Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SR051). Western blot analysis of human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cell lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human MDA-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) Antibody (#ASR-051), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of human THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cell lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human MDA-231 breast adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) Antibody (#ASR-051), (1:400).
3,4. Anti-Semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) Antibody, preincubated with Semaphorin 3A/SEMA3A Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SR051).
Semaphorins are members of a large family of proteins controlling a variety of processes in the central nervous system (CNS) during development such as cell migration and axonal growth cone guidance but are also expressed in other tissues. Their common feature is a conserved 500 amino acid “sema” domain. There are currently eight defined classes of semaphorins; classes 2 and 3 are secreted proteins while others are GPI-linked or transmembrane proteins.
Semaphorin 3A protein is an elongated disc shaped molecule with dimensions of 60X70X45 angstrom and a molecular weight of 65 kDA. The semaphorin fold is a variation of the β propeller topology with seven blades radially arranged around a central axis. Each blade averages 70 amino acids and contains a four stranded antiparallel sheet. The large size of this protein derives from the secondary structural elements attached to each blade.
Two units of Semaphorin 3A create a functional Semaphorin 3A dimer. Neuropilin-1 binds to semaphorin-3A and competes with semaphorin dimerization indicating that the neuropilin-1 binding region of Semaphorin 3A is in proximity to the dimerization site1. Another Semaphorin binding molecule is plexin-1. It does not bind to semaphorin alone but only in a complex with Neuropilin-1. Interestingly, this complex has higher affinity to semaphorin than Neuropilin-1 alone. In addition, binding of neuropilin-1 does not change non-neuronal cell morphology while the combination of Neuropilin-1 and plexin-1 induces an alteration in adherent cells2.
The downregulation of Semaphorin expression was found to be linked to many pathological conditions of the CNS such as ischemia, degenerative diseases and multiple sclerosis and it was also found that semaphorin-3A encourages tumor growth in multiple myeloma3.
