Overview
- Peptide (C)SRGHSGRYWAEISD, corresponding to amino acid residues 113-126 of human SIGMAR1 (Accession Q99720). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) liver membranes:1,2. Anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Antibody (AIP-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse (lanes 2 and 4) liver membranes:1,2. Anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Antibody (AIP-006), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Antibody, preincubated with Sigma-1 Receptor Blocking Peptide (#BLP-IP006).
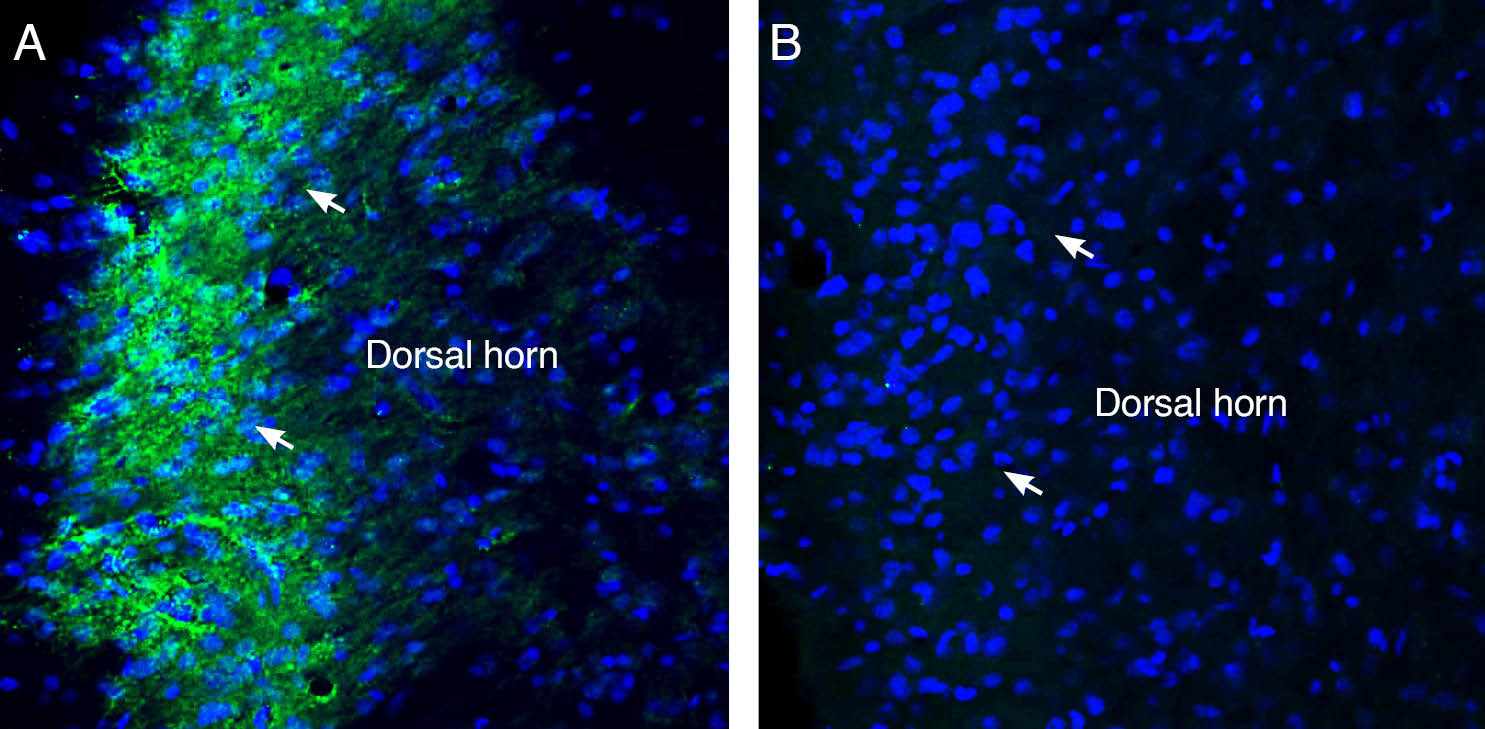 Expression of Sigma-1 Receptor in rat spinal cord.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat spinal cord sections with Anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Antibody (#AIP-006), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Sigma-1 Receptor immunoreactivity (green) appeared in the superficial layer of the dorsal horn (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Sigma-1 Receptor Blocking Peptide (BLP-IP006), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of Sigma-1 Receptor in rat spinal cord.Immunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat spinal cord sections with Anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Antibody (#AIP-006), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. Sigma-1 Receptor immunoreactivity (green) appeared in the superficial layer of the dorsal horn (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with Sigma-1 Receptor Blocking Peptide (BLP-IP006), suppressed staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Mansour, A. et al. (1995) Trends. Neurosci. 18, 22.
- Jin, J.L. et al. (2015) Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 8, 4808.
Sigma receptors were first identified as a subtype of opioid receptors. The different members of the family are differentially distributed in various parts of the CNS and are responsible for a vast range of functions and behaviors1. Today, sigma receptors are mostly considered to be a separate receptor family with two main subtypes characterized.
The sigma-1 receptor is encoded by a gene baring the same name and is a protein of 223 amino acids with two transmembrane domains and a typical endoplasmic reticulum localized signal near its short N terminus. Sigma receptors are mostly detected in the central nervous system with a high density in the spinal cord, pons, medulla oblongata, red nucleus, cerebellum and hippocampus.
Sigma-1 is mainly localized on the mitochondrial associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM), forming a BiP chaperone structure with high sensitivity to the calcium ion. When activated by agonists such as cocaine or analgesics, sigma-1 receptors separate from BiP and translocate from MAM to other parts of the cell. Through regulation of inositol triphosphate (IP3) receptors, NMDA receptors, dopamine receptors and voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, sigma-1 receptors can influence TCA cycle, oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, neuron plasticity and the release of various neurotransmitters.
The exact etiology and pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease is not fully understood. A few hypotheses suggest the involvement of Sigma-1 in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. The suggested mechanisms include protection from Aβ toxicity, prevention of Tau protein hyperphosphorylation and the upregulation of acetylcholine release2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Sigma-1 Receptor Antibody (#AIP-006) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot analysis. It has been designed to recognize SIGMAR1 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Western blot of human differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Tested in cells transfected with SIGMAR1 siRNA. Sun, Y. et al. (2020) Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 41, 1245.
