Overview
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Specifications
- Peptide (C)SKFISDRESRRSLTNSH, corresponding to amino acid residues 41-57 of rat SLC38A1 (Accession Q9JM15). Cytoplasmic, N-terminus.
Applications
- Rat brain, rat placenta, mouse brain, human glioblastoma U-87 MG and human T-cell leukemia Jurkat cell lines, (1:200-1:4000).
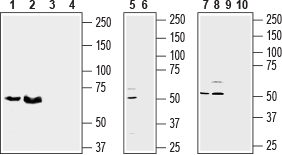 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3), rat placenta (lanes 2 and 4), (1:800), mouse brain membrane (lanes 5 and 6), (1:200), human U-87 MG (lanes 7 and 9), and human Jurkat (lanes 8 and 10), (1:500) cell lysates:1, 2, 5, 7, 8. Anti-SLC38A1 Antibody (#ANT-184).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3), rat placenta (lanes 2 and 4), (1:800), mouse brain membrane (lanes 5 and 6), (1:200), human U-87 MG (lanes 7 and 9), and human Jurkat (lanes 8 and 10), (1:500) cell lysates:1, 2, 5, 7, 8. Anti-SLC38A1 Antibody (#ANT-184).
3, 4, 6, 9, 10. Anti-SLC38A1 Antibody, preincubated with SLC38A1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NT184).
Scientific Background
SNAT1 (SLC38A1, Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 1) is a 486 amino acids system A type sodium symporter that catalyzes the electrogenic Na+-dependent uptake of glutamine, among other substrates. SNAT1 is thought to be responsible for glutamine uptake into neurons1.
SNAT1 belongs to the β-family of solute carriers that includes three SLC families, SLC32, SLC36, and SLC38. SNAT1 is a member of the SLC38 family that includes 11 members, SNAT1 to SNAT11.
SNAT1 and SNAT2 are expressed in neurons and in glial cells all over the central nervous system, with high expression in perivascular glial profiles and lower expression in astrocytes of the cerebral parenchyma. This supports a role in controlling the amino acid permeability at the blood-brain barrier2. SNAT1 also acts as a positive regulator of mTORC1 signaling pathway in neurons and plays an important pathological role in the mechanism underlying neuronal survival after ischemia3. It was also shown to be up-regulated in specific types of cancer4.
The structure of SNAT proteins is predicted to have a 5+5 inverted repeat fold typical of the bacterial LeuT, with intracellular N-terminus and extracellular and C-terminal tail5.
