Overview
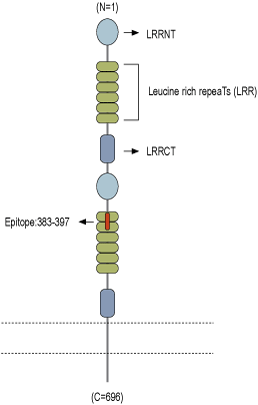
- Peptide (C)RDNKIHSIRKSHFVD, corresponding to amino acid residues 383-397 of mouse Slitrk1 (Accession Q810C1). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain synaptosomal fraction (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and mouse brain synaptosomal fraction (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with Slitrk1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SR081).
 Multiplex staining of Slitrk1 and KV2.1 in rat parietal cortexImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:200) and Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:200). A. Slitrk1 staining (red) appears in profiles of pyramidal neurons. B. KV2.1 staining (green) is detected in profiles of pyramidal neurons. C. Merge of the two images shows colocalization in several neurons (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of Slitrk1 and KV2.1 in rat parietal cortexImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:200) and Guinea pig Anti-KV2.1 Antibody (#APC-012-GP), (1:200). A. Slitrk1 staining (red) appears in profiles of pyramidal neurons. B. KV2.1 staining (green) is detected in profiles of pyramidal neurons. C. Merge of the two images shows colocalization in several neurons (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).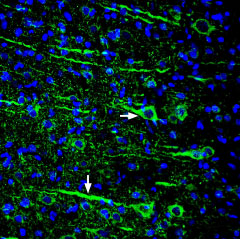 Expression of Slitrk1 in rat cortexImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections using Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. Slitrk1 staining (green) in the rat parieto-temporal cortex is detected in pyramidal neurons (horizontal arrow) and their dendrites (vertical arrow). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of Slitrk1 in rat cortexImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen rat brain sections using Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081), (1:300), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. Slitrk1 staining (green) in the rat parieto-temporal cortex is detected in pyramidal neurons (horizontal arrow) and their dendrites (vertical arrow). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
- Aruga, J. and Mikoshiba, K. (2003) Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 24, 117.
- Beaubien, F. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 27343.
Neurites are key morphological features of neurons, and are classified into axons and dendrites. Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains are often found in neurite development-controlling proteins. Slitrk proteins are leucine-rich repeat containing transmembrane proteins, parts of which are similar to Slit and neurotrophin receptor.
All six members of the Slitrk family, including Slitrk1, contain putative hydrophobic signal sequences and membrane-spanning regions. Slitrk1 is strongly expressed in the subventricular zone of the cerebral cortex, the pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus and in the thalamus and hypothalamus1.
Slitrk1, can regulate synapse formation between hippocampal neurons. Slitrk1 is enriched in postsynaptic fractions and is localized to excitatory synapses. Overexpression of Slitrk1 in hippocampal neurons increases the number of synaptic contacts on these neurons. Furthermore, decreased expression of Slitrk1 in hippocampal neurons leads to a reduction in the number of excitatory, but not inhibitory, synapses formed in hippocampal neuron cultures. In addition, different leucine rich repeat domains of the extracellular region of Slitrk1 are necessary to mediate interactions with Slitrk binding partners of the LAR receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase family, and to promote dimerization of Slitrk1. In addition, Slitrk1 binds with PSD-95 through its intracellular tail. Thus, through PSD-95, Slitrk1 regulates signaling of NMDA and AMPA receptors2.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Slitrk1 (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-081) is a highly selective antibody directed against an epitope of the mouse protein. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. The antibody recognizes an extracellular epitope, and can potentially be used for detecting the protein in living cells. It has been designed to recognize Slitrk1 from mouse, human, and rat samples.
Applications
Citations
- Western blot and immunohistochemistry of mouse brain. Tested in mice microinjected with Slitrk1 siRNA.
Du, J-C. et al. (2024) Ann. Neurol. 95, 174.
