Overview
- Peptide (C)ELGLSKLKESGKHQS, corresponding to amino acid residues 141-155 of rat SARAF (Accession Q6AYN2). Intracellular, lumen.

 Western blot analysis of rat pancreas (lanes 1 and 2), Mouse MS1 endothelial cells (lanes 3 and 5) and human PANC1 pancreatic carcinoma cells (lanes 4 and 6) lysates:1,3,4. Anti-TMEM66 Antibody (#ACC-067), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of rat pancreas (lanes 1 and 2), Mouse MS1 endothelial cells (lanes 3 and 5) and human PANC1 pancreatic carcinoma cells (lanes 4 and 6) lysates:1,3,4. Anti-TMEM66 Antibody (#ACC-067), (1:500).
2,5,6. Anti-TMEM66 Antibody, preincubated with TMEM66 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC067).
 Expression of TMEM66 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-TMEM66 Antibody (#ACC-067), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. TMEM66 immunoreactivity (green) appears in the molecular layer (MOL) and in neurons of the purkinje cell layer (P, arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TMEM66 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC067), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). G = granule layer.
Expression of TMEM66 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections with Anti-TMEM66 Antibody (#ACC-067), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. TMEM66 immunoreactivity (green) appears in the molecular layer (MOL) and in neurons of the purkinje cell layer (P, arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TMEM66 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC067), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). G = granule layer.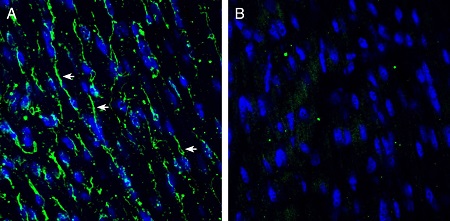 Expression of TMEM66 in mouse heartImmunohistochemical staining of frozen mouse heart sections with Anti-TMEM66 Antibody (#ACC-067), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. TMEM66 staining (green) appears along the lateral wall of muscle fibers (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TMEM66 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC067), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Expression of TMEM66 in mouse heartImmunohistochemical staining of frozen mouse heart sections with Anti-TMEM66 Antibody (#ACC-067), (1:200), followed by goat anti-rabbit-AlexaFluor-488. A. TMEM66 staining (green) appears along the lateral wall of muscle fibers (arrows). B. Pre-incubation of the antibody with TMEM66 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC067), suppresses staining. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
TMEM66 (Transmembrane protein 66, also known as SOCE-associated regulatory factor, SARAF) is a regulatory protein of cellular Ca2+ homeostasis, encoded by the TMEM66 gene. TMEM66 is an ER resident protein, which responds to cytosolic Ca2+ elevation after ER Ca2+ refilling.
TMEM66 is highly conserved in vertebrates. In mammals it is ubiquitously expressed with high transcript levels in the immune and neuronal tissues. The TMEM66 structure contains validated signal peptide and a putative single membrane spanning domain, a serine-proline rich domain and arginine rich regions followed by a cluster of basic residues at its C-terminal tail1.
Store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) is an important Ca2+ influx pathway across plasma membranes in many non-excitable cells. In this pathway, intracellular Ca2+ release through IP3 receptors stimulated by a variety of agonists, results in reduction of Ca2+ concentration in the lumen of the endoplasmic or sarcoplasmic reticulum. SARAF negatively regulates store operated calcium entry into cells and protects cells from calcium overfilling1,2.
STIM, Ca2+ sensor, and Orai, the channel pore forming subunit proteins have been identified as the essential components enabling the reconstitution of Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channels that mediate SOCE. Knock-out of Orai1 or STIM1 in mice and mutations evoke SOCE in lymphocytes and other cells2,3.
Findings show that dysregulation of Ca2+ homeostasis is associated with a plethora of pathological conditions including neurodegenerative diseases, skeletal, muscular and cardiovascular disorders2. Inherited defects in SOCE due to mutations in genes of the Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channel complex causes patients to suffer from a severe form of immunodeficiency that is due to defects in the function of T cells, NK cells and potentially other immune cells3.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-TMEM66 Antibody (#ACC-067) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of rat transmembrane protein 66. The antibody can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize TMEM66 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse sample:
La Russa D. et al. (2020) Neuroscience. 441, 8.
- Mouse sample:
La Russa D. et al. (2020) Neuroscience. 441, 8.
