Overview
- Peptide DKDTTRRIHVSTDQD(C) corresponding to amino acid residues 320-335 of human Sortilin (Accession Q99523). Extracellular domain.
- Mouse J774 macrophage and human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells (2.5 µg).
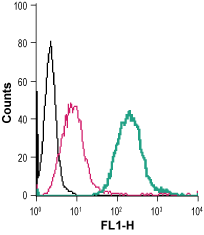 Cell surface detection of Sortilin in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of Sortilin in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-Sortilin (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ANT-009-F), (2.5 µg). Cell surface detection of Sortilin in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of Sortilin in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + rabbit IgG isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Anti-Sortilin (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ANT-009-F), (2.5 µg).
Sortilin is a member of the Vps10p family named for a yeast gene that is involved in trafficking between the trans-golgi network and the vacuole. In mammals sortilin has been shown to play an important role in golgi to endosome and golgi to lysosome trafficking. Sortilin is also known as neurotensin receptor 3 (NTS3), one of the receptors for the peptide neurotransmitter neurotensin that exerts several biological functions ranging from the regulation of dopamine transmission and pain in the central nervous system to its functioning as a local hormone affecting the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, sortilin has been lately identified as a co-receptor of p75NTR for the binding of the proneurotrophins proNGF and proBDNF. Moreover, Sortilin expression was found to be essential for proNGF and proBDNF-induced neuronal cell death.
Sortilin is a type I membrane protein with a large extracellular domain that includes 8 bacterial neuraminidase repeats (BNRs), a single transmembrane region and a short cytoplasmic tail. The protein is expressed in several tissues, most notably in brain, spinal cord, skeletal muscle and adipocytes.
Paradoxically for its role as either a neurotensin receptor or a p75NTR co-receptor for proneurotrophins, about 90% of sortilin is retained in intracellular compartments with only about 10% reaching the cell surface. It has been speculated, that changes in the cellular environment may increase cell surface expression of sortilin.
