Overview
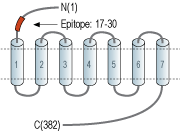
- Peptide SDYVNYDIIVRHYN(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 17-30 of human S1PR1 (Accession P21453). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Western blot analysis of (RAEC) rat aortic endothelial cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and A-10 Rat thoracic aorta smooth muscle (lane 2 and 4) cell lysates:1,2. Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-011), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of (RAEC) rat aortic endothelial cell line lysates (lanes 1 and 3) and A-10 Rat thoracic aorta smooth muscle (lane 2 and 4) cell lysates:1,2. Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-011), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with S1PR1/EDG1 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-SR011).
 Expression of Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded rat lung sections using Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-011), (1:100). Staining is present in vascular smooth muscle (black arrows) but not in the muscular layer of bronchi (red arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 in rat lungImmunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded rat lung sections using Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-011), (1:100). Staining is present in vascular smooth muscle (black arrows) but not in the muscular layer of bronchi (red arrows). Hematoxilin is used as the counterstain.
 Expression of Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 in mouse 3T3 cellsCell surface detection of Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 in mouse live 3T3 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-011), (1:50), (red). B. DAPI is used for nuclear staining (blue). Merged image of A and B.
Expression of Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 in mouse 3T3 cellsCell surface detection of Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 in mouse live 3T3 cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-011), (1:50), (red). B. DAPI is used for nuclear staining (blue). Merged image of A and B.
- Pyne, S. and Pyne, N.J. (2000) Biochem. J. 349, 385.
- Hla, T. et al. (2001) Science 294, 1875.
- Takuwa, Y. et al. (2002) J. Biochem. 131, 767.
- Rosen, H. et al. (2009) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 743.
- Rosen, H and Liao, J. (2003) Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 7, 461.
Lysophospholipids constitute a group of important lipid mediators; lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) a glycerolysophospholipid and sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), a lysosphingolipid. Sphingosine 1-phosphate is a bioactive lipid derived from metabolism of sphingomyelin1. Sphingosine 1-phosphate is implicated in the regulation of many cellular functions including proliferation, apoptosis, survival, adhesion, differentiation, and migration2. Sphingosine 1-phosphate exerts its activity through five distinct G-protein-coupled receptors, (also named endothelial differentiation gene receptors - EDG); S1PR1 (EDG-1), S1PR2 (EDG-5), S1PR3 (EDG-3), S1PR4 (EDG-6), and S1PR5 (EDG-8)3.
Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) is ubiquitously expressed. S1PR1 mRNA is detected in the brain, heart, spleen, liver, lung, thymus, kidney, skeletal muscle and lymphoid tissues4. Knockout of the gene encoding S1PR1 is lethal and therefore makes in vivo studies difficult5.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-S1PR1 (EDG1) (extracellular) Antibody (#ASR-011) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize S1PR1 from human, rat, and mouse samples.

