Overview
- Peptide (C)EGTRESAINVAEGKK, corresponding to amino acid residues 208-222 of rat Stomatin-like protein 2 (Accession Q4FZT0). Intracellular.
- Rat and mouse brain lysates, human brain neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y, human prostate carcinoma DU 145, human pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 and human acute lymphoblastic leukemia MOLT-4 cell lines (1:400-1:4000).
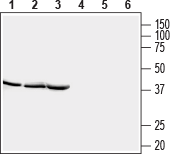 Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and rat skeletal muscle lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-STOML2/SLP-2 Antibody (#AIP-002), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat brain lysate (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and rat skeletal muscle lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-STOML2/SLP-2 Antibody (#AIP-002), (1:400).
4-6. Anti-STOML2/SLP-2 Antibody, preincubated with STOML2/SLP-2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-IP002). Western blot analysis of human brain neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y (lanes 1 and 5), human prostate carcinoma DU 145 (lanes 2 and 6), human pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 (lanes 3 and 7) and human acute lymphoblastic leukemia MOLT-4 (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-STOML2/SLP-2 Antibody (#AIP-002), (1:800).
Western blot analysis of human brain neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y (lanes 1 and 5), human prostate carcinoma DU 145 (lanes 2 and 6), human pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 (lanes 3 and 7) and human acute lymphoblastic leukemia MOLT-4 (lanes 4 and 8):1-4. Anti-STOML2/SLP-2 Antibody (#AIP-002), (1:800).
5-8. Anti-STOML2/SLP-2 Antibody, preincubated with STOML2/SLP-2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-IP002).
Stomatin-like protein 2 (STOML2, SLP-2) is a key protein on the mitochondrial inner membrane and a member of the stomatin superfamily. STOML2 is widely expressed in human tissues such as the brain, lung, and kidneys and interacts with prohibitin-1 and 2. It plays an important role in numerous physiological processes including organizing sphingolipid and cholesterol-rich lipid rafts, regulating ion channel conductance, and linking other integral membrane proteins to the peripheral cytoskeleton1,2.
STOML2 shares a consensus stomatin signature sequence that defines the stomatin gene family. However, it lacks a NH2-terminal hydrophobic domain shared by other members3.
Studies show that STOML2 expression is upregulated in various human cancer tissues including gastric cancer, endometrial adenocarcinoma, and breast cancer. The protein may play an important role in the incidence and development of tumor and it is suggested that SLP-2 is a potential oncogene. Knockdown of STOML2 protein significantly restrains the viability, migration, and invasion of hepatoma cell line1,2.
