Overview
- Peptide CRQTGNT(S)KELRD, corresponding to amino acid residues 178-190 of rat synaptophysin (Accession P07825). 2nd intravesicular loop.

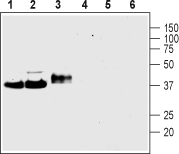 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody (#ANR-013), (1:400).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cell line lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody (#ANR-013), (1:400).
4-6. Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody, preincubated with Synaptophysin Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR013).
 Expression of Synaptophysin in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) frozen sections using Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody (#ANR-013), (1:100). SYP (red) is expressed in DRG neurons. Hoechst 33342 (blue) shows nuclear staining and is used as the counterstain.
Expression of Synaptophysin in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) frozen sections using Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody (#ANR-013), (1:100). SYP (red) is expressed in DRG neurons. Hoechst 33342 (blue) shows nuclear staining and is used as the counterstain. Colocalization of NaV1.8 and Synaptophysin in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of rat DRG frozen section using Anti-NaV1.8 (SCN10A)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#ASC-016-AR) and Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody (#ANR-013). A. NaV1.8 staining (red). B. SYP staining (green). C. Merged image demonstrates a partial overlap in the distribution of NaV1.8 and SYP within the DRGs. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Colocalization of NaV1.8 and Synaptophysin in rat DRGImmunohistochemical staining of rat DRG frozen section using Anti-NaV1.8 (SCN10A)-ATTO Fluor-594 Antibody (#ASC-016-AR) and Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody (#ANR-013). A. NaV1.8 staining (red). B. SYP staining (green). C. Merged image demonstrates a partial overlap in the distribution of NaV1.8 and SYP within the DRGs. DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
- Jahn, R. et al. (1985) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 4137.
- Navone, F. et al. (1986) J. Cell Biol. 103, 2511.
- Wiedenmann, B. and Franke, W.W. (1985) Cell 41, 1017.
- Johnston, P.A. et al. (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264, 1268.
- Kwon, S.E. and Chapman, E.R. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 35658.
- Kwon, S.E. and Chapman, E.R. (2011) Neuron 70, 847.
- Schmitt, V. et al. (2009) Neuroscience 162, 234.
- Tarpey, P.S. et al. (2009) Nat. Genet. 41, 535.
Synaptophysin is the major integral membrane protein of small synaptic vesicles1-3. It belongs to a family of proteins which includes synaptogyrin and synaptoporin. The protein contains 4 transmembrane domains and cytoplasmic N- and C-termini4. There are two intravesicular loops that contain disulfide bonds. The protein is N-glycosylated on the first intravesicular loop, a modification important for the synaptic vesicle targeting of synaptophysin. Indeed, a mutant form of the protein, unable to undergo glycolysation, leads to the accumulation of the protein in the cell body of neurons indicating that N-glycosylation is required for the synaptic localization of synaptophysin5. The C-terminal tail is extensively phosphorylated on Tyr residues. However, the biological significance of the post-translational modification is not yet determined6.
Although exact and specific role of synaptophysin remains a mystery, a study suggests that the protein is required for efficient endocytosis of synaptic vesicles in cultured hippocampal neurons6.
Since synaptophysin is exclusively detected in synaptic vesicles, it is widely used as a marker for presynaptic vesicles.
Genetic screening in humans and behavioral studies in rodents show that loss of synaptophysin expression or expression of a truncated form of the protein may be attributed to mental retardation and/or learning deficits7,8. Interestingly though, synaptic transmission in synaptophysin knockout mice remains normal6.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-Synaptophysin Antibody (#ANR-013) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. It can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize synaptophysin from mouse, rat, and human samples.
Applications
Citations
- Mouse brain lysate.
Yang, P. et al. (2016) Exp. Neurol. 279, 178.
