Overview
- GST fusion protein with the sequence MKDRTQELRTAKDSDDDDDVTVTVDRDRFMDEFFEQVEEIRGFIDKIAENVEEVKRKHSAILASPNPDEKTKEELEELMSDIKKTANKVRSKLKSIEQSIEQEEGLNRSSADLRIRKTQH STLSRKFVEVMSEYNATQSDYRERCKGRIQRQLEITGRTTTSEELEDMLESGNPAIFASGIIMDSSISKQALSEIETRHSEIIKLENSIRELHDMFMDMAMLVESQGEMIDRIEYNVEHAVDYVERAVSDTKKAVKYQSKARRKK, corresponding to amino acid residues 1-265 of rat syntaxin 1A (Accession P32851). Intracellular, N-terminus.
- Rat brain membranes (1:1000).
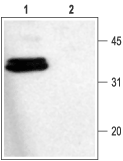 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-Syntaxin 1 Antibody (ANR-002), (1:1000).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-Syntaxin 1 Antibody (ANR-002), (1:1000).
2. Anti-Syntaxin 1 Antibody, preincubated with Syntaxin 1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-NR002).
- Rat brain sections.
Syntaxin 1 is a member of the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) protein superfamily. The family includes 36 members in humans and is characterized by the SNARE motif, an evolutionarily conserved stretch of 60–70 amino acids that are arranged in heptad repeats1,2.
SNARE proteins are involved in exocytosis and intracellular vesicle trafficking and are essential for cell growth, hormone secretion and neurotransmission, processes that require rapid, targeted, and regulated membrane fusion1,2.
SNAREs can be roughly divided into vesicular (v-SNAREs) and target (t-SNAREs) based on their distribution on the transport vesicle or target membrane respectively. Thus, assembly of cognate v-/t-SNAREs between two opposing membranes generates trans-SNARE complexes, which bring the lipid bilayers in close proximity and drive membrane fusion.
Syntaxin 1, like most SNAREs, is a type IV membrane protein with a relatively large N-terminus containing the SNARE motif located in the cytoplasmic side and a transmembrane domain located close to the C-terminus that functions as an anchor1,2.
Syntaxin 1 has been extensively studied for its role on neuronal and neuroendocrine cell exocytosis where it functions as the plasma membrane protein t-SNARE, which together with the vesicular v-SNARE protein VAMP and the membrane-associated SNAP-25 (synaptosome-associated protein 25 kDa), forms a trimeric, four-helical complex, which drives fusion of the two opposing bilayers1,2.
Syntaxin 1 together with SNAP-25 is the target of the neurotoxin botulinum neurotoxin type C (BoNT/C) which following proteolytic degradation of the proteins causes inhibition of neurotransmitter release 3.
