Overview
- Peptide (C)TPREPNRWAVEREG, corresponding to amino acid residues 581-594 of rat TauT (Accession P31643). Intracellular, C-terminus.
- Mouse brain membranes, rat small intestine lysate and human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia and HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cell lysates (1:200-1:1000).
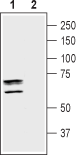 Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody (#AGT-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain membranes:1. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody (#AGT-006), (1:200).
2. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody, preincubated with Taurine Transporter/SLC6A6 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GT006). Western blot analysis of rat small intestine lysate:1. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody (#AGT-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat small intestine lysate:1. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody (#AGT-006), (1:200).
2. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody, preincubated with Taurine Transporter/SLC6A6 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GT006). Western blot analysis of human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody (#AGT-006), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and human HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cell lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1,2. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody (#AGT-006), (1:200).
3,4. Anti-Taurine Transporter (SLC6A6) Antibody, preincubated with Taurine Transporter/SLC6A6 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-GT006).
Taurine (2-aminoethane-sulfonice acid) is one of the most abundant amino acids found in the human body. It is involved in cell regulation and modulates the concentration of intracellular free calcium. It also plays a substantial role in many other functions varying from neurotransmission in the central nervous system to promotion of cell differentiation in the brain to cytoprotection against oxidative stress1.
Taurine is not used for protein synthesis, and in addition to its uptake in nutrition, it can be synthesized in pancreatic mammalian cells by cysteine dioxygenase and sulfinoalanine decarboxylase enzymes2.
Taurine is found mainly in organs such as the brain, retina and muscle tissue.
The uptake of taurine is conducted through the taurine transporter (TauT). The energy for passage through the transporter is derived by Na+ and Cl- concentration similar to the uptake of other amino acids3. TauT also transports GABA, albeit with a lower affinity. The transporter has twelve transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini.
TauT expression is regulated by cAMP which was found to increase its regulation in MDCK cells and also by PKC via means of post-translational modification. PKC activation leads to reduced taurine transport4. PKC is believed to phosphorylate the highly conserved serine-322 position in the transporter.
Taurine deficiency is linked to cardiomyopathies in the hearts of cats and to a decrease in cardiac muscle sensitivity to calcium5 and better understanding of its transport may improve research of these diseases.
