Overview
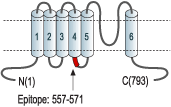
- Peptide QLYDKGYTSKEQKDC, corresponding to amino acid residues 557-571 of human TRPC1 (Accession P48995). Intracellular.
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes:1. Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010), (1:200).
2. Anti-TRPC1 Antibody, preincubated with TRPC1 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC010).
- Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (Ahmmed, G.U. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 20941.).
 Expression of TRPC1 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum frozen sections using Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010). A. TRPC1 (red) appears in Purkinje cells (arrows) and in the molecular (Mol) and granule (Gran) layers. B. Staining with mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV) in the same brain section. C. Confocal merge of TRPC1 and PV demonstrates partial co-localization in the Purkinje and the molecular layers.
Expression of TRPC1 in mouse cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of mouse cerebellum frozen sections using Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010). A. TRPC1 (red) appears in Purkinje cells (arrows) and in the molecular (Mol) and granule (Gran) layers. B. Staining with mouse anti-parvalbumin (PV) in the same brain section. C. Confocal merge of TRPC1 and PV demonstrates partial co-localization in the Purkinje and the molecular layers.
- BAE-1 (Bovine aortic endothelium) cells (1:200) (Antoniotti, S. et al. (2002) FEBS Lett. 510, 189.).
Human U373 MG cells (1:80) (Barajas, M. et al. (2008) J. Neurosci. Res. 86, 3456.).
- Moran, M.M. et al. (2004) Current Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 362.
- Clapham, D.E. et al. (2003) Pharmacol. Rev. 55, 591.
- Clapham, D.E. (2003) Nature 426, 517.
- Padinjat, R. and Andrews, S. (2004) J. Cell. Sci. 117, 5707.
- Huang, C.L. (2004) J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15, 1690.
- Liu, X. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11337.
The Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) superfamily is one of the largest ion channel families and consists of diverse groups of proteins. In mammals, about 28 genes encode the TRP ion channel subunits. The mammalian TRP superfamily comprises six subfamilies known as the TRPC (canonical), TRPV (vanilloid), TRPM (melastatin), TRPML (mucolipins), TRPP (polycystin) and the TRPA (ANKTM1) ion channels.1-4
The TRPC subfamily consists of seven proteins named TRPC1 to 7, which can be further divided into four subgroups based on their sequence homology and functional similarities:
1) TRPC1
2) TRPC4 and TRPC5
3) TRPC3, TRPC6, TRPC7
4) TRPC2.2,5
They are highly expressed in the central nervous system and to a lesser extent in peripheral tissues.
TRPC1 was the first mammalian TRP protein that was reported to form an ion channel.2 It can co-assemble with other TRPC subunits (TRPC3, TRPC4, TRPC5) to form heterotetramers whose properties are distinct from that of their homomeric form. The existence of the TRPC1 homomers has not been established as yet.1-3
The TRPC1, TRPC4 and TRPC5 can be activated either by Ca2+ store depletion or by GPCR stimulation pathways, while TRPC3, TRPC6 and TRPC7 form non-selective cationic channels that are activated by the stimulation of GPCRs. TRPC1, 4 and TRPC5 are assumed to form components of store operated channels in some cell types such as salivary gland cells, endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells.6
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the human protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize TRPC1 from human, mouse, and rat samples.

Knockout validation of Anti-TRPC1 Antibody in mouse substantia nigra.Western blot analysis of mouse substantia nigra lysates using Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010). TRPC1 is not detected in TRPC1-/- lysates.Adapted from Sun, Y. et al. (2017) J. Neurosci. 37, 3364. with permission of the Society of Neuroscience.
Applications
Citations
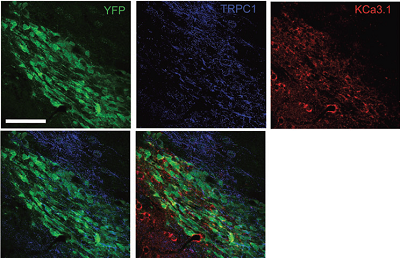 Multiplex staining of KCa3.1 and TRPC1 in mouse brain.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051) and Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010). YFP denotes neuroblasts. TRPC1 staining (blue) is detected in neuroblasts and outside neuroblasts as well (in astrocytes). KCa3.1 (red) is detected in neuroblasts. Merged image of all three staining (lower right panel) demonstrates the partial co-localization between the three.
Multiplex staining of KCa3.1 and TRPC1 in mouse brain.Immunohistochemical staining of mouse brain sections using Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051) and Anti-TRPC1 Antibody (#ACC-010). YFP denotes neuroblasts. TRPC1 staining (blue) is detected in neuroblasts and outside neuroblasts as well (in astrocytes). KCa3.1 (red) is detected in neuroblasts. Merged image of all three staining (lower right panel) demonstrates the partial co-localization between the three.
Adapted from Turner, K.L. and Sontheimer, H. (2014) with permission of Oxford University Press.
- Western blot analysis of human SH-SY5Y cell lysate and mouse brain lysate. Also tested on TRPC1-/- cells.
Sun, Y. et al. (2017) J. Neurosci. 37, 3364.
- Rat endothelial cells (EC) and smooth muscle cells (SMC).
Liang, M. et al. (2018) Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 40, 39. - Mouse primary cerebellar granule cell lysate.
Du, T. et al. (2017) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 10, 305. - Human SH-SY5Y cell lysate and mouse brain lysate. Also tested on TRPC1-/- cells.
Sun, Y. et al. (2017) J. Neurosci. 37, 3364. - Human lung mast cells (1:200).
Wajdner, H.E. et al. (2017) Physiol. Rep. 5, e13166. - Mouse primary astrocytes.
Wang, W. et al. (2017) Neurochem. Res. 42, 762. - Human HepG2 liver carcinoma cell lysate (1:1000).
Badr, H. et al. (2016) Front. Pharmacol. 7, 19. - Mouse brain lysate (1:200).
Du, L.L. et al. (2016) Mol. Neurobiol. 54, 1992. - Human MCF-7 breast cancer cell lysate.
Faouzi, M. et al. (2016) Oncotarget 7, 36419. - Rat pulmonary artery lysates.
Jiang, H.N. et al. (2016) Biomed. Pharmacol. 82, 20. - Rat PASMC lysate.
Jiang, Q. et al. (2016) Am. J. Physiol. 311, C136. - Rat PASMC cell lysate (1:1000).
Lin, A.H. et al. (2016) Cardiovasc. Res. 111, 94. - Mouse embryonic fibroblast cells lysates.
Ryazantseva, M. et al. (2016) J. Neurochem. 136, 1085. - Human epithelial cells (1:200).
Bertrand, J. et al. (2015) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 765, 337. - Mouse Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cell lysate.
Vigont, V. et al. (2015) Front. Physiol. 6, 337. - Mouse MLE-12 lung epithelial cell lysate.
Zhou, X. et al. (2015) Mol. Cell. Biol. 35, 16. - Rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) lysate.
Jiang, Q. et al. (2014) PLoS ONE 9, e107135. - Human HT29 colon adenocarcinoma cell lysate.
Sobradillo, D. et al. (2014) J. Biol. Chem. 289, 28765. - Rat heart lysate.
Chen, M.S. et al. (2013) Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 32, 951. - Mouse brain lysate.
Feng, S. et al. (2013) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 11011. - Rat distal pulmonary smooth muscle cell lysate (PASMCs).
Zhang, Y. et al. (2013) Am. J. Physiol. 304, C833.
- Rat IEC-6 cell lysate.
Rathor, N. et al. (2014) Physiol. Rep. 2, e12193. - Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
Ahmmed, G.U. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 20941.
- Rat brain sections.
Martinez-Galan, J.R. et al. (2018) Front. Neuroanat. 12, 15. - Mouse brain sections.
Turner, K.L. and Sontheimer, H. (2013) Cereb. Cortex 24, 2388. - Rat DRGs (1:500).
Boudes, M. et al. (2013) PLoS ONE 8, e69550.
- Rat primary cultured fetal and neonatal ventricular myocytes (1:100).
Jiang, Y. et al. (2014) Cell Tissue Res. 355, 201. - Human U373 MG cells (1:80).
Barajas, M. et al. (2008) J. Neurosci. Res. 86, 3456. - BAE-1 (Bovine aortic endothelium) cells (1:200).
Antoniotti, S. et al. (2002) FEBS Lett. 510, 189.
- Cuddapah, V.A. et al. (2013) Cell Calcium 53, 187.
- Ng, L.C. et al. (2012) Am. J. Physiol. 303, C1156.
