Overview
- Peptide (C)NGTDPYKPK(S)PESD, corresponding to amino acid residues 999-1012 of human TRPM2 (Accession O94759). 3rd extracellular loop.
- Mouse and rat brain lysates; human THP-1 monocytic leukemia and HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell lysates (1:200-1:1000).
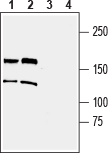 Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-TRPM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-128), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 3) and rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 4):1, 2. Anti-TRPM2 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-128), (1:200).
3, 4. Anti-TRPM2 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with TRPM2 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC128).
- Rat brain sections.
- Human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells (2.5 µg).
The mammalian melastatin-related transient receptor potential (TRPM) is a subfamily of the TRP family. The family was named after the first discovered member, melastatin (TRPM1) whose gene was identified in metastatic and benign melanomas1-3.
The TRPM family consists of eight members: TRPM1-8 that can be further divided into four pairs: TRPM1 and TRPM3; TRPM2 and TRPM8; TRPM4 and TRPM5; and TRPM6 and TRPM71,2.
The TRPM proteins share structural homology with other members of the TRP superfamily channels; six putative transmembrane domains, and cytoplasmic N- and C-termini. However, due to their long N- and C-termini they are also named the long TRP channel family1-3.
The C-terminal regions of three TRPM members (TRPM2, TRPM6 and TRPM7) are occupied by enzymatic domains. Almost all the C-terminal region of TRPM2 has an enzymatic domain with sequence similarities to Nudix hydrolases (cleave mononucleotide and dinucleotide polyphosphates2,4.
TRPM2 (LTRpC2, TrpC7) is a Ca2+-permeable, nonselective cation channel that is predominantly expressed in various regions of the brain, where it is preferentially localized in microglial cells, the host macrophages of the central nervous system and is also expressed in other tissues, including spleen, heart, liver, lung, and bone marrow. Several splice variants of TRPM2 have been identified5,3.
