Overview
- Peptide KNKDDMPYMSQAQEIH(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 816-831 of human TRPM3 (Accession Q9HCF6). 1st extracellular loop.
- Rat brain membrane, rat and mouse brain lysate (1:200).
 Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 4), rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-TRPM3 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-050), (1:200).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membrane (lanes 1 and 4), rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and mouse brain lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Anti-TRPM3 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-050), (1:200).
4-6. Anti-TRPM3 (extracellular) Antibody, preincubated with TRPM3 (extracellular) Blocking Peptide (#BLP-CC050).
- Mouse optic nerves sections (Papanikolaou, M. et al. (2017) Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 2993.).
- Mouse astrocyte culture (Papanikolaou, M. et al. (2017) Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 2993.).
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are relatively non-selective ion channels enabling the exchange of cations down their electrochemical gradient. This exchange enables the intracellular rise in Na+ and Ca2+ concentration and ultimately in the cell membrane depolarization, important for action potential propagation and muscle contraction1. They are activated by an extremely broad range of stimuli namely, temperature, voltage, pH, endocrine factors as well as signaling molecules2.
The TRP channel family is composed of 28 members divided in 7 subgroups: TRPV, TRPC, TRPM, TRPA, TRPN, TRPP and TRPML. All members of the TRP family have 6 transmembrane (TM) domains, and a pore domain between the fifth (S5) and sixth (S6) transmembrane domains. In general, TRP channels enable the passage of either Na+ or Ca2+ ions with little or no preference. However, some channels do exhibit some selectivity. Also, TRP channels do not display the positive charges in the S4 voltage-sensing domain like most voltage sensitive channels, although they do display voltage dependency3. In addition, TRP channels have in the C-terminal intracellular region to the S6 domain a TRP domain comprising 25 amino acids that is more or less conserved among most TRP channels. Within the TRP domain, there is a TRP box composed of six amino acids, and TRP box 2 – a proline rich domain1,3. The TRP domain seems to be responsible for the binding of PIP2, a phospholipid important for the regulation of channel activity4.
The TRPM subfamily consists of 8 members divided in to three major groups: TRPM1/3, TRPM4/5, and TRPM6/7. TRPM2 and TRPM8 are not included in any of the groups since they are quite different even with respect to each other. TRPM3 is alternatively spliced into active variants5,6. TRPM3a1 and TRPM3a2 in mouse are monovalent and divalent-selective channels, respectively. This differential selectivity strongly suggests that their cellular role depends on the relative expression of each variant type. In addition, both splice variants display constitutive outwardly rectifying currents. They somewhat resemble TRPM6 and TRPM7 channels such that their currents are inhibited by intracellular Mg2+ 1.
TRPM3 is highly expressed in the kidney, and to a lesser extent in the brain, testis, and spinal cord7.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
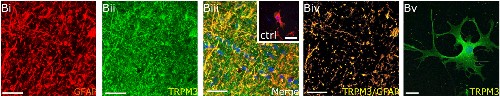
Expression of TRPM3 in mouse optic nerves.Bi-Biv. Immunohistochemical staining of mouse optic nerve sections using Anti-TRPM3 (extracellular) Antibody (#ACC-050). TRPM3 staining (green) is highly expressed in astrocytes and co-localizes with GFAP, an astrocyte marker. Bv. Immunocytochemical staining of explant cultures also shows expression of TRPM3 (green).Adapted from Papanikolaou, M. et al. (2017) Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 2993. with permission of Springer Nature publishing.
